SEO Traffic Dropped After Migration? Step-by-Step Recovery Guide (2026)

Website migration is one of the highest-risk SEO activities. If your organic traffic dropped suddenly after a migration, you are not alone — and in most cases, the damage is recoverable.
This guide is a complete, real-world recovery framework used by SEO consultants to restore rankings after:
- Domain migrations
- CMS changes
- URL restructuring
- HTTPS moves
- Large-scale redesigns
We will not give theory. We will show exactly what to check, what to fix, and in what order.
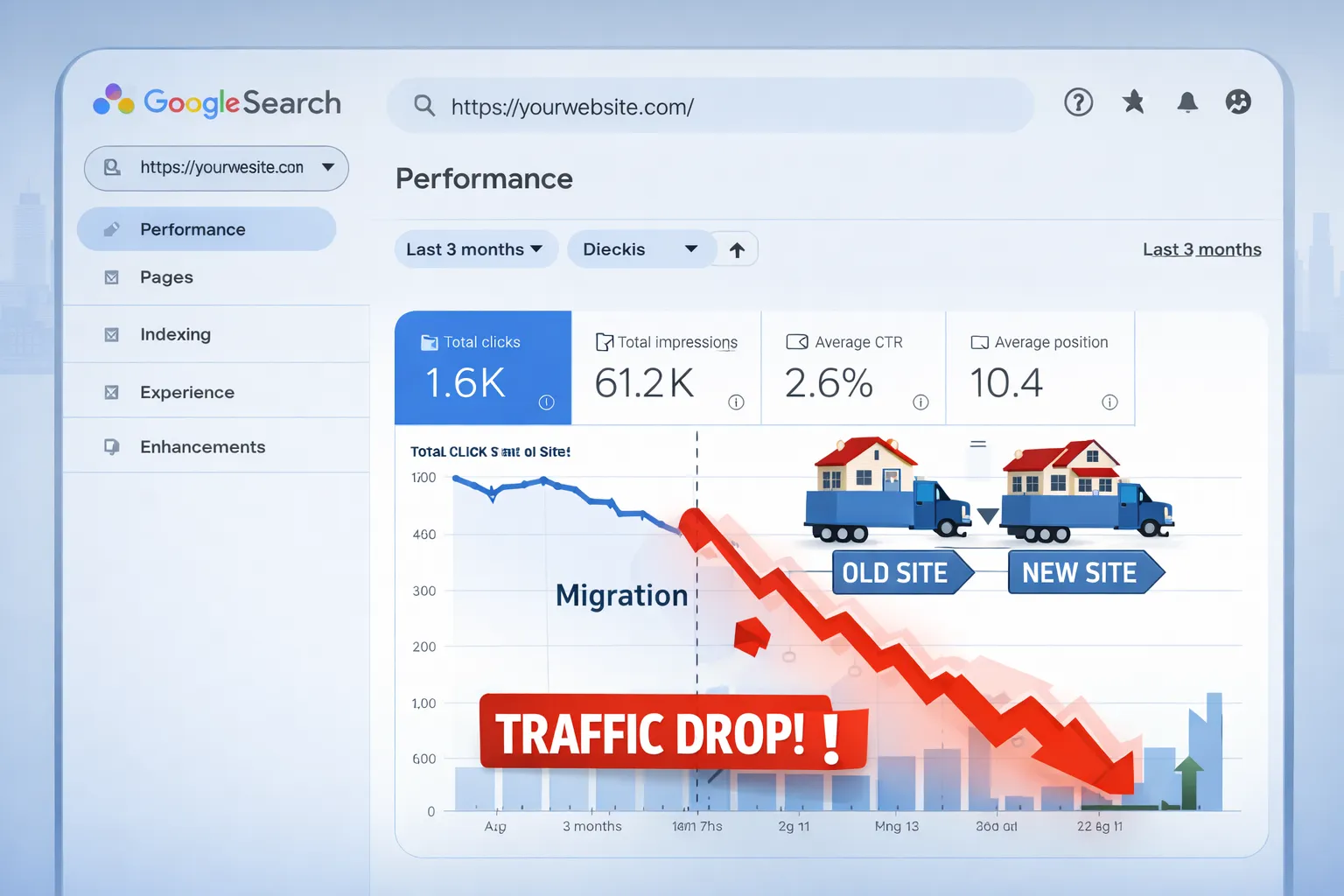
PART A: Diagnose Why SEO Traffic Dropped After Migration
Before fixing anything, you must understand why the drop happened. Blind fixes often make the situation worse.
Google does not penalize migrations — but it reacts brutally to broken signals.
SEO migration mistakes1️⃣ Is This a Normal Post-Migration Fluctuation or a Real Problem?
Some volatility after migration is normal. The key is to identify whether you’re seeing:
301 redirect strategy- Temporary recalculation (normal)
- Structural signal loss (serious)
Normal fluctuation signs:
- Small keyword position changes (±3–5)
- Traffic stabilizes within 7–14 days
- Pages still indexed
Critical warning signs:
- Traffic drops 30–70%
- Pages disappear from index
- GSC shows “Page with redirect” or “Not indexed”
2️⃣ Confirm the Drop Using Google Search Console (Not GA4 Alone)
Never rely only on analytics tools. Search Console is Google’s truth source.
Check these reports:
- Performance → Search results (compare before vs after migration)
- Pages → Indexing status
- Settings → Crawl stats
If impressions drop sharply, Google is reducing visibility — not users.
3️⃣ Identify the Exact Date & Trigger
Pinpoint the exact day traffic dropped.
migration SEO checklistMatch it against:
- Migration launch date
- Redirect deployment
- robots.txt changes
- Canonical or noindex updates
A sudden cliff usually means:
- Redirects missing or broken
- Pages blocked from indexing
- Canonical conflicts
4️⃣ Check Page Indexing Status (This Is Critical)
Go to GSC → Pages.
Red flags include:
- Page with redirect
- Crawled – currently not indexed
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical
- Soft 404
If important pages fall into these buckets, Google is ignoring them.
5️⃣ Compare Indexed URLs Before vs After Migration
Use this comparison:
- Old sitemap URL count
- Current indexed page count
If the number dropped significantly:
- Pages are blocked
- Redirects failed
- Google lost trust in signals
6️⃣ Check Branded vs Non-Branded Traffic
If branded searches still appear but non-branded keywords vanished:
Page with redirect issue- Authority signals were damaged
- Topical relevance weakened
This almost always points to:
- Redirect relevance issues
- Internal linking damage
7️⃣ Diagnose Traffic Loss Type
| Symptom | Likely Cause |
|---|---|
| Sudden site-wide drop | Redirect / robots / canonical issue |
| Only some pages lost | URL mapping errors |
| Impressions down, clicks stable | Ranking recalculation |
| Pages indexed but no rankings | Authority transfer failure |
End of Part A
At this point, you should clearly know:
- When traffic dropped
- Which pages were affected
- Whether the issue is structural
Do not attempt fixes yet. In Part B, we repair the most common cause of migration SEO failure: redirects, URLs, and site architecture.
PART B: Fix Redirects, URLs & Site Architecture (The #1 Recovery Factor)
If SEO traffic dropped after migration, redirect failure is responsible in more than 70% of real-world cases.
This section focuses on restoring:
- Lost link equity
- Keyword relevance
- Crawl efficiency
- Google’s trust in URL relationships
Important: Redirect fixes usually deliver the fastest recovery wins.
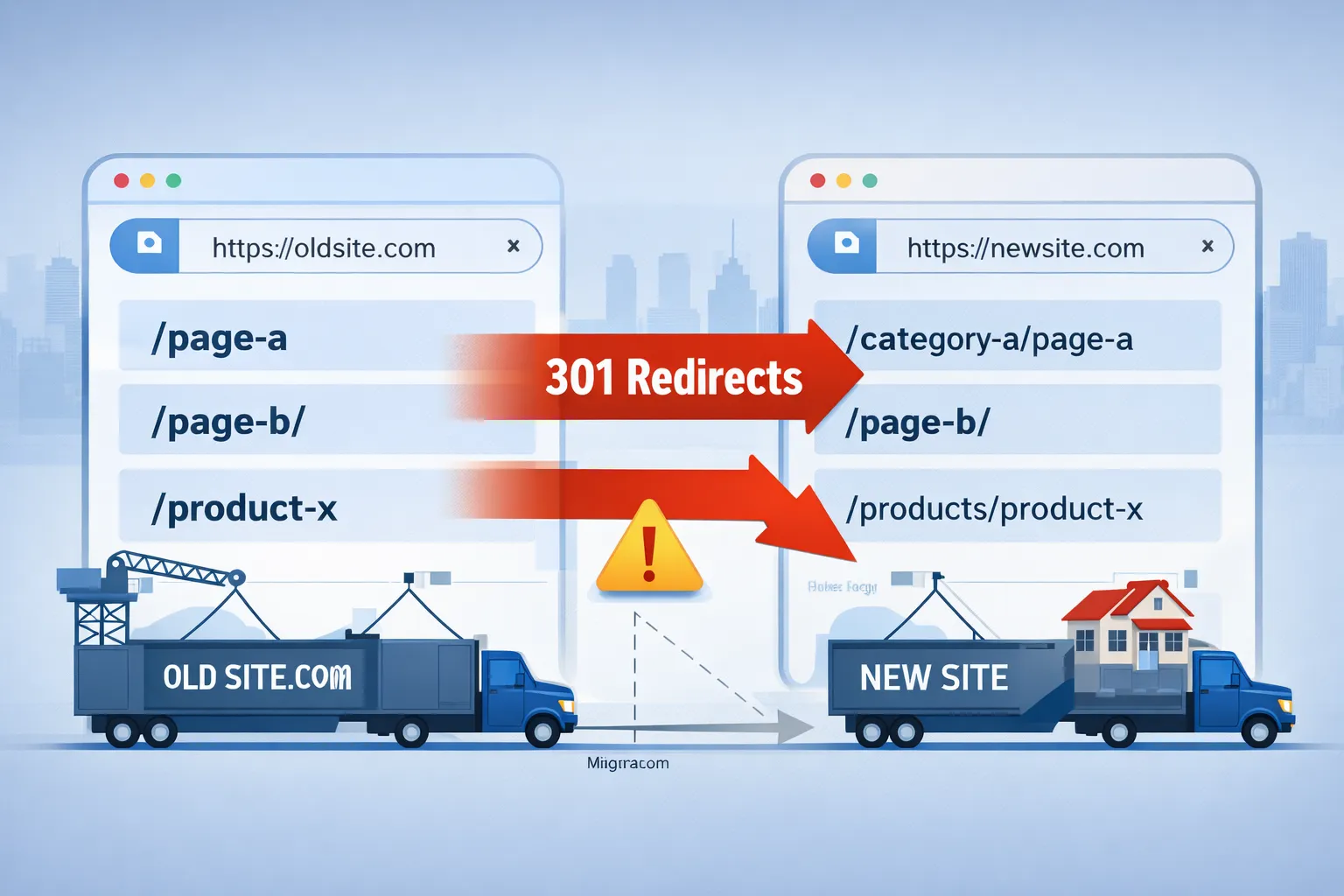
1️⃣ Audit All 301 Redirects (No Exceptions)
You must audit redirects using a crawler — not manual checks.
What to export:
- Old URL
- Final destination URL
- Status code
- Redirect hops
Critical rules:
- Only 301 redirects (never 302)
- One hop only
- No redirect chains
2️⃣ Eliminate Redirect Chains Immediately
Redirect chains are silent SEO killers.
Bad example:
/old-page → /temp-page → /new-page
Google may stop following chains after multiple hops.
SEO audit guide3️⃣ Stop Homepage Redirect Abuse
Redirecting many URLs to the homepage causes:
- Loss of keyword relevance
- Soft 404 signals
- Ranking collapse
Correct approach:
- Blog → related blog
- Category → matching category
- Service → equivalent service
4️⃣ Fix “Page with Redirect” Indexing Issues
If Google reports Page with redirect, it means:
- Internal links still point to old URLs
- Sitemap contains redirected URLs
- Canonicals are incorrect
Fix checklist:
- Update internal links to final URLs
- Remove redirected URLs from sitemap
- Ensure canonicals point to final URL
5️⃣ Validate Canonical Tags After Migration
Canonical conflicts can completely neutralize redirects.
Common migration mistakes:
- Canonical pointing to old domain
- Multiple canonicals
- Missing self-canonical
6️⃣ Repair Internal Linking Structure
Internal links distribute authority across your site.
After migration, most sites suffer from:
- Links pointing to redirected URLs
- Broken anchor text
- Lost contextual relevance
Fix order:
- Update top navigation links
- Fix footer links
- Fix contextual blog links
7️⃣ Normalize URL Versions (Duplication Control)
Post-migration duplication often includes:
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- WWW vs non-WWW
- Trailing slash vs non-slash
Required actions:
- Force one canonical URL format
- Redirect all variants
- Ensure sitemap uses canonical version
8️⃣ Fix Pagination & Parameter URLs
Broken pagination creates crawl chaos.
Common issues:
- /page/2 returns 404
- Sort/filter parameters indexed
- Duplicate category URLs
9️⃣ Re-submit Clean XML Sitemap
Your sitemap must contain:
- Only 200-status URLs
- Canonical URLs only
- No redirected pages
Submit it again in Google Search Console.
10️⃣ Validate Crawl Path Efficiency
After migration, Google must:
- Reach pages quickly
- Understand hierarchy
- Follow clean paths
Flatten overly deep URLs where possible.
End of Part B
By the end of this phase, you should have:
- Clean 301 redirects
- No redirect chains
- Correct canonicals
- Restored internal linking
In Part C, we move to the next layer: indexing recovery, content preservation, and technical SEO fixes.
PART C: Fix Indexing, Content Loss & Technical SEO Issues
After redirects, the second biggest reason SEO traffic drops after migration is indexing failure combined with content dilution.
Even when redirects are correct, Google may:
- Delay re-indexing
- Ignore updated URLs
- Devalue rewritten or shortened content
This section focuses on restoring indexability, relevance, and trust.
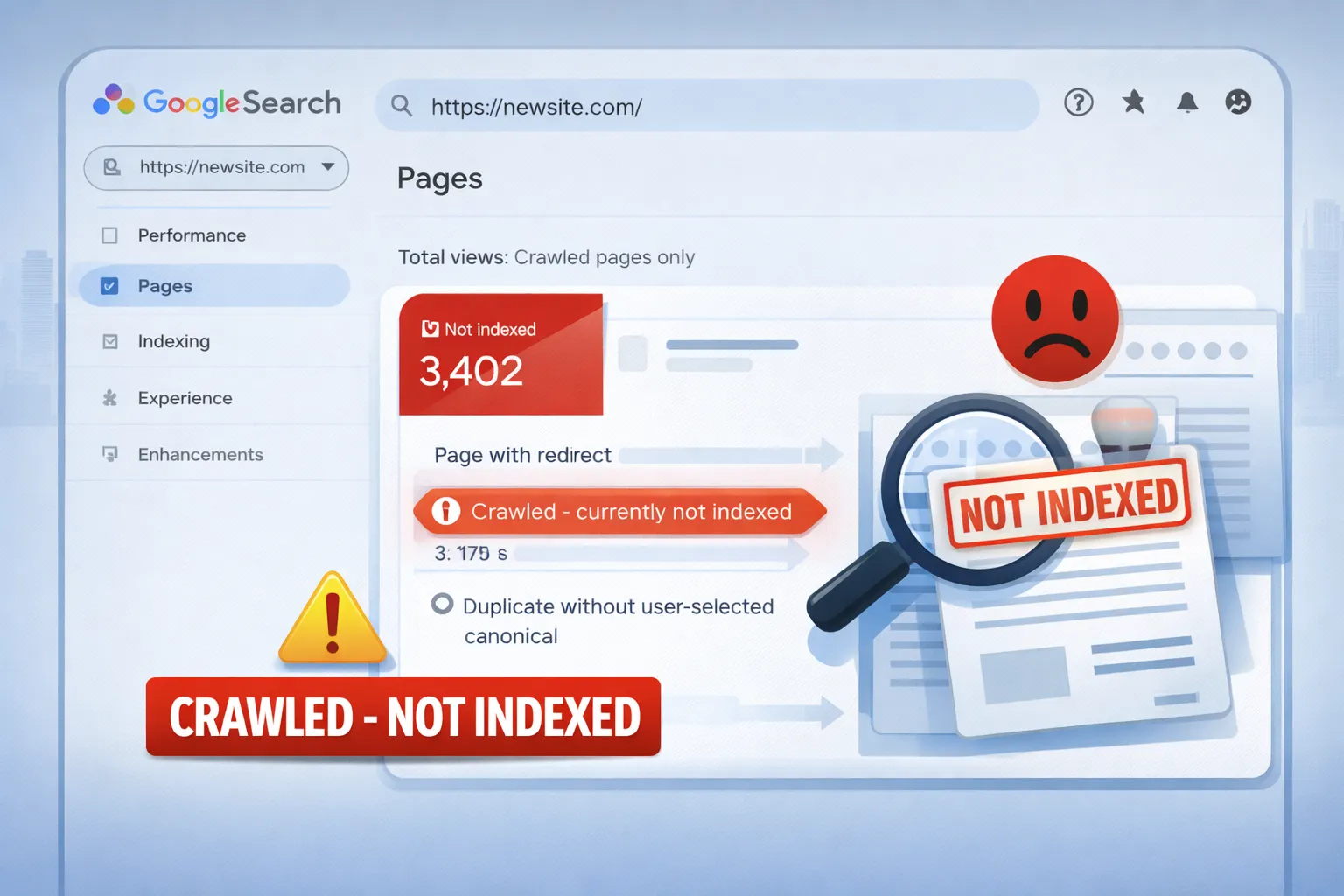
1️⃣ Diagnose Indexing Status in Google Search Console
Go to Pages → Indexing and segment URLs into:
- Indexed
- Crawled – currently not indexed
- Discovered – currently not indexed
- Excluded
What this tells you:
- Crawled but not indexed → Quality / duplication issues
- Discovered but not indexed → Crawl budget or internal linking issues
2️⃣ Fix “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Pages
This issue explodes after migrations.
Main causes:
- Thin or shortened content
- Duplicate intent pages
- Weak internal linking
- Redirected internal references
Recovery checklist:
- Restore original content length
- Merge overlapping pages
- Add internal links from strong pages
- Ensure self-referencing canonicals
3️⃣ Prevent Content Loss & Keyword Cannibalization
During redesigns, content is often:
- Shortened
- Rewritten without keyword intent
- Split into multiple weak pages
This causes immediate ranking drops.
Fix:
- Compare old vs new content word count
- Restore removed sections
- Preserve heading structure (H1–H3)
4️⃣ Repair Keyword Intent Mismatches
Google ranks pages by intent, not just keywords.
Common migration mistake:
/blog/seo-audit-guide → /services/seo-solutions
This breaks ranking alignment.
5️⃣ Audit Robots.txt & Meta Robots Directives
Many sites accidentally block themselves post-migration.
Check for:
Disallow: /- Noindex meta tags
- X-Robots-Tag headers
6️⃣ Fix JavaScript Rendering & Hidden Content
Modern migrations often introduce JS-heavy frameworks.
Google may not render:
- Lazy-loaded content
- Content behind user actions
- Delayed API-rendered sections
Fix:
- Ensure HTML contains critical content
- Avoid JS-only headings
- Test rendered HTML using URL Inspection
7️⃣ Recover Core Web Vitals Regression
New designs often hurt performance.
Common regressions:
- Large hero images (LCP)
- Layout shifts (CLS)
- Heavy JS blocking interaction (INP)
Immediate fixes:
- Compress hero images
- Reserve space for dynamic elements
- Defer non-critical scripts
8️⃣ Validate Structured Data After Migration
Schema often breaks when templates change.
Common failures:
- Missing Article schema
- Broken FAQ markup
- Invalid JSON-LD syntax
Fix schema errors to restore rich results and CTR.
9️⃣ Restore Crawl Budget Efficiency
Google allocates crawl budget based on:
- Site health
- Internal linking
- Duplicate URLs
Post-migration cleanup:
- Remove junk URLs
- Fix infinite filters
- Block useless parameters
10️⃣ Request Re-indexing Strategically
Do NOT submit thousands of URLs manually.
Best approach:
- Submit sitemap
- Request indexing for priority pages only
- Let internal links do the rest
End of Part C
At this stage, you should have:
- Recovered indexability
- Restored content depth
- Fixed technical blockers
- Stabilized crawl behavior
In Part D, we finalize recovery with: monitoring, timelines, KPIs, FAQs (50+), and long-term prevention.
PART D: Post-Migration Monitoring, Recovery Timeline & Prevention
At this stage, your site is technically fixed — but SEO recovery is not instant. Google needs time to crawl, process, reassess, and re-rank.
This section explains:
- Exactly how long recovery takes
- What metrics to track (and ignore)
- How to prevent future migration disasters
- 50+ FAQs answering real migration recovery questions
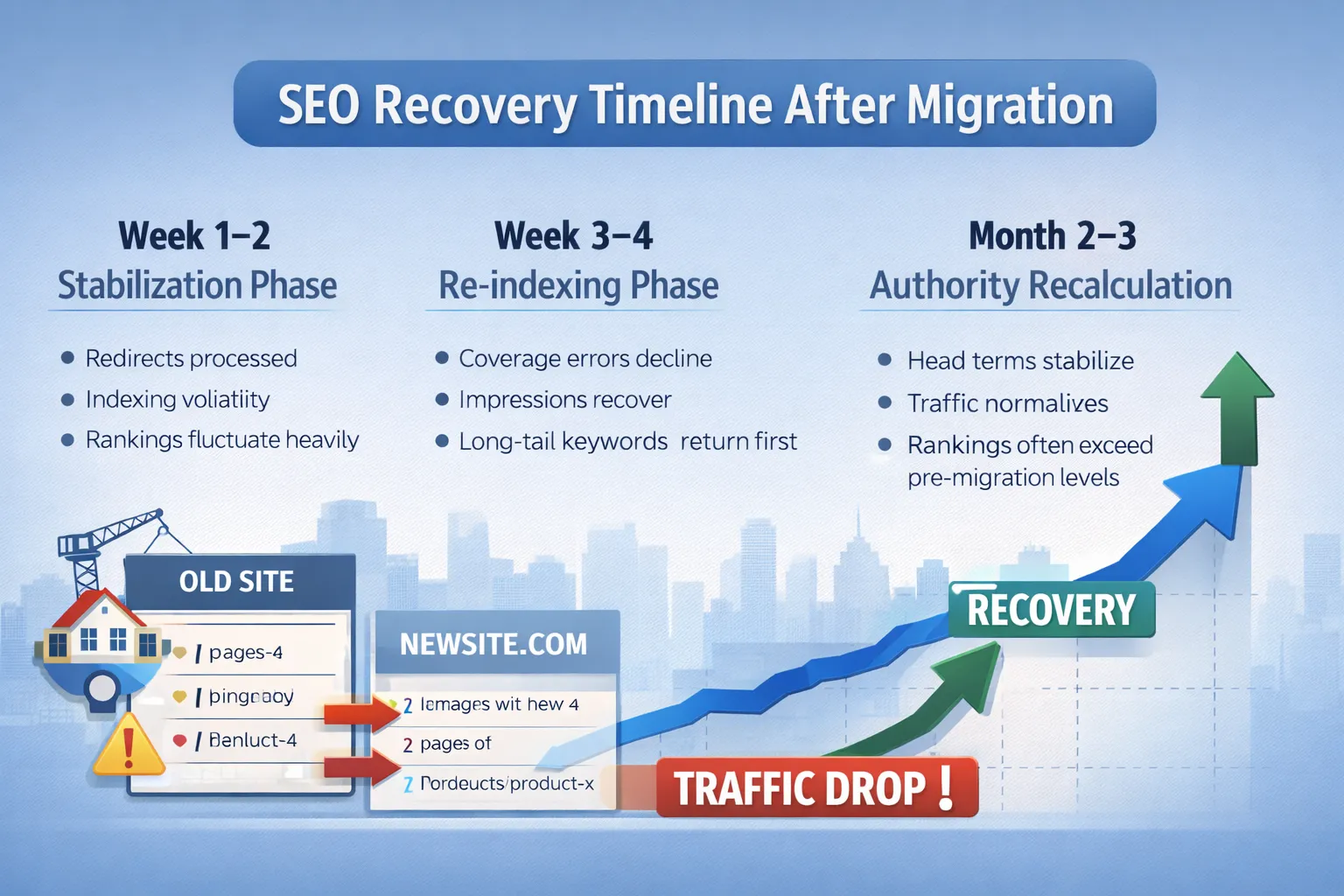
📅 SEO Recovery Timeline After Migration (Realistic Expectations)
Week 1–2: Stabilization Phase
- Redirects processed
- Indexing volatility
- Rankings fluctuate heavily
What to do:
- Fix critical errors only
- Monitor GSC daily
- Avoid panic changes
Week 3–4: Re-indexing Phase
- Coverage errors decline
- Impressions recover
- Long-tail keywords return first
What to do:
- Strengthen internal linking
- Restore missing content
- Optimize top pages only
Month 2–3: Authority Recalculation
- Head terms stabilize
- Traffic normalizes
- Rankings often exceed pre-migration levels
📊 SEO Metrics That Actually Matter Post-Migration
Track these:
- Indexed pages count
- Impressions (not rankings)
- Crawl stats
- Organic landing page traffic
Ignore temporarily:
- Daily keyword fluctuations
- Third-party tool volatility
- Short-term CTR drops
🚫 What NOT to Do During SEO Recovery
- Do not remove redirects
- Do not rewrite content aggressively
- Do not change URL structure again
- Do not block crawling to “fix things”
SEO Traffic Drop After Migration — FAQs
General Recovery
Q1. Is traffic drop after migration normal?
A: Yes. Temporary traffic drops are common after migrations while Google reassesses indexing and ranking signals.
Q2. How long until rankings return?
A: In most cases, rankings begin recovering within 2–8 weeks if migration issues are fixed correctly.
Q3. Can traffic drop permanently?
A: Yes. If critical issues like broken redirects or blocked indexing are not resolved, traffic loss can become permanent.
Q4. Should I revert the migration?
A: No. Rolling back often causes more harm. It is better to fix issues and move forward.
Q5. Are redirects always required?
A: Yes. Proper 301 redirects are mandatory whenever URLs change during a migration.
Indexing Issues
Q6. Why are pages crawled but not indexed?
A: This usually happens due to thin content, duplication, weak internal linking, or low-quality signals.
Q7. Should I force indexing in Google Search Console?
A: No. You should fix the root cause instead of forcing indexing requests.
Q8. How many URLs should I submit for indexing?
A: Only submit your most important priority pages, not the entire site.
Q9. Can an XML sitemap fix indexing issues?
A: A sitemap helps Google discover pages faster but does not fix quality or technical problems by itself.
Q10. Does internal linking help with indexing?
A: Yes. Strong internal linking significantly improves crawlability and indexing.
Redirects
Q11. Are 302 redirects bad for migrations?
A: Yes. Temporary redirects do not reliably transfer ranking signals during migrations.
Q12. How long should redirects be kept?
A: Redirects should remain active for at least 12 months, and longer for high-value URLs.
Q13. Can redirect chains hurt SEO?
A: Yes. Redirect chains dilute link equity and reduce crawl efficiency.
Q14. Should redirects point to the homepage?
A: No. Redirects should always go to the most relevant equivalent page.
Q15. Can incorrect redirects kill rankings?
A: Absolutely. Poor redirect mapping is one of the biggest causes of post-migration traffic loss.
Content
Q16. Does rewriting content during migration hurt SEO?
A: Often yes. Major content changes can break keyword relevance and ranking signals.
Q17. Should content stay identical after migration?
A: During migration, it is best to keep content unchanged until rankings stabilize.
Q18. Can content length impact recovery?
A: Yes. Reducing content depth frequently leads to ranking drops.
Q19. Should I merge pages after migration?
A: Only merge pages that target overlapping search intent.
Q20. Can missing headings hurt SEO?
A: Yes. Headings help search engines understand structure and relevance.
Technical SEO
Q21. Can robots.txt block SEO recovery?
A: Yes. A single incorrect rule can prevent Google from crawling your site.
Q22. Can JavaScript affect indexing?
A: Yes. Heavy or poorly implemented JavaScript can delay or prevent indexing.
Q23. Do Core Web Vitals matter after migration?
A: Yes. Performance regressions can negatively impact rankings and user experience.
Q24. Is schema required for SEO recovery?
A: Schema is not required but can improve visibility and click-through rates.
Q25. Should HTTPS migration worry me?
A: Only if redirects or canonical tags are implemented incorrectly.
Monitoring
Q26. How often should I check Google Search Console?
A: Daily monitoring is recommended during the first month after migration.
Q27. Should I track keywords daily?
A: No. Weekly tracking provides more reliable trend data.
Q28. Can GA4 data lag after migration?
A: Yes. Analytics tools often lag behind actual indexing changes.
Q29. Should I analyze server logs?
A: For large websites, log analysis is extremely valuable.
Q30. What is crawl budget?
A: Crawl budget is how often and how deeply Google crawls your website.
Advanced
Q31. Does backlink value transfer after migration?
A: Yes. Proper 301 redirects pass most link equity.
Q32. Should I update backlinks to new URLs?
A: Only update high-value backlinks where possible.
Q33. Can domain migration fully recover?
A: Yes. Many sites fully recover and even grow after migration.
Q34. Is staging site indexing dangerous?
A: Extremely. It can cause duplicate content and trust issues.
Q35. Should I pause publishing new content?
A: Yes. Focus on stabilization before publishing aggressively.
Prevention
Q36. What is the best way to avoid traffic loss?
A: Careful planning and pre-migration testing.
Q37. Should SEO be involved early in migration?
A: Always. SEO involvement should begin at the planning stage.
Q38. Can checklists prevent migration issues?
A: Yes. Structured checklists reduce human error significantly.
Q39. Should migrations be phased?
A: If possible, phased migrations reduce risk.
Q40. Is rollback a good solution?
A: Rarely. Fixing issues forward is almost always safer.
Misc
Q41. Can ad performance drop after migration?
A: Yes. Landing page changes often affect paid campaigns.
Q42. Can CTR change after migration?
A: Yes. Titles, URLs, and rich results may change.
Q43. Are impressions more important than clicks early?
A: Yes. Impressions indicate visibility recovery.
Q44. Does Google reset trust after migration?
A: No. Google reassesses signals rather than resetting trust.
Q45. Is patience required during recovery?
A: Yes. SEO recovery takes time even after fixes.
Final
Q46. Can SEO improve after migration?
A: Yes. Many sites come back stronger with better structure.
Q47. Should I hire an SEO expert?
A: For large or complex sites, professional help is highly recommended.
Q48. Is migration SEO risky?
A: Yes, but risks are manageable with proper execution.
Q49. Are all traffic drops SEO-related?
A: No. Seasonality, tracking, and algorithm changes can also impact traffic.
Q50. Can I future-proof migrations?
A: Yes. Following a proven migration framework dramatically reduces risk.
Final Conclusion
Website migration SEO checklistSEO traffic drops after migration are recoverable.
Most failures are caused by:
- Poor redirect execution
- Indexing blockers
- Content dilution
- Panic decisions
Follow this guide step by step and you not only recover — you often come back stronger than before.
Request a Free SEO Recovery Audit →
