SEO Migration Mistakes That Kill Rankings (2026 Guide)
Last updated: 2026-01-01 · 18 min read
Website migration is one of the highest-risk activities in SEO. Even experienced teams lose traffic simply because
they overlook critical steps. This guide breaks down the most common SEO migration mistakes and shows
you exactly how to avoid them.
This is not theory. These mistakes come from real migrations involving CMS changes, domain moves,
URL restructuring, and platform upgrades.

Why SEO Migrations Fail So Often
Most SEO failures during migration happen before the site even launches.
Teams rush development, ignore SEO input, or assume Google will “figure it out.”
Unfortunately, Google does not forgive migration errors easily.
- Lost rankings
- Traffic drops of 30–70%
- Deindexed pages
- Broken backlinks
Understanding what not to do is just as important as following best practices.
When preparing for large structural changes or platform upgrades, it’s critical to follow a structured
website migration SEO checklist
to prevent crawl errors, ranking loss, and traffic drops.
PHASE 1: Pre-Migration SEO Mistakes
Pre-migration planning determines 80% of your migration success. Skipping this phase is the biggest mistake of all.
❌ Mistake #1: Migrating Without an SEO Audit
Many websites migrate without documenting what currently works. This leads to losing:
- Top-ranking pages
- High-traffic URLs
- Keyword relevance
- Internal link equity
Before any migration, you must complete a full SEO audit covering:
- Indexed pages
- Ranking keywords
- Backlinks
- Site architecture
👉 Related guide: Complete SEO Audit Checklist
Fix: Export data from Google Search Console, GA4, and crawl tools before migration.
❌ Mistake #2: No URL Mapping Document
One of the most damaging mistakes is not mapping old URLs to new URLs.
Google needs a clear relationship between old and new pages.
Without URL mapping:
- Pages return 404
- Backlinks lose value
- Rankings disappear
Every migration must include a spreadsheet with:
- Old URL
- New URL
- Status code
- Priority
Fix: Create URL mapping before development starts — not after launch.
❌ Mistake #3: Changing Too Many Things at Once
Many teams change all of the following simultaneously:
- Domain
- CMS
- Design
- Content
- URL structure
This makes it impossible to identify what caused ranking drops.
Fix: Phase migrations when possible. Limit changes to what’s necessary.
❌ Mistake #4: Ignoring Internal Linking Structure
Internal links distribute authority across your site. During migration, these often:
- Break
- Redirect unnecessarily
- Point to outdated URLs
This weakens page authority and crawl efficiency.
👉 Related guide: Technical SEO Best Practices
❌ Mistake #5: Not Setting a Migration Freeze
Publishing content during migration causes:
- Missed redirects
- Indexing conflicts
- Tracking errors
Fix: Freeze content updates until migration completes and stabilizes.
End of Phase 1
Phase 1 focused on the planning mistakes that cause the biggest SEO disasters.
In Phase 2, we will cover URL structure, redirect, and architecture mistakes that destroy rankings.
PHASE 2: URL, Redirect & Site Architecture SEO Mistakes
Even with perfect planning, most SEO migrations fail during implementation.
Phase 2 covers the most destructive technical mistakes related to
URLs, redirects, and site structure — the core of SEO equity transfer.
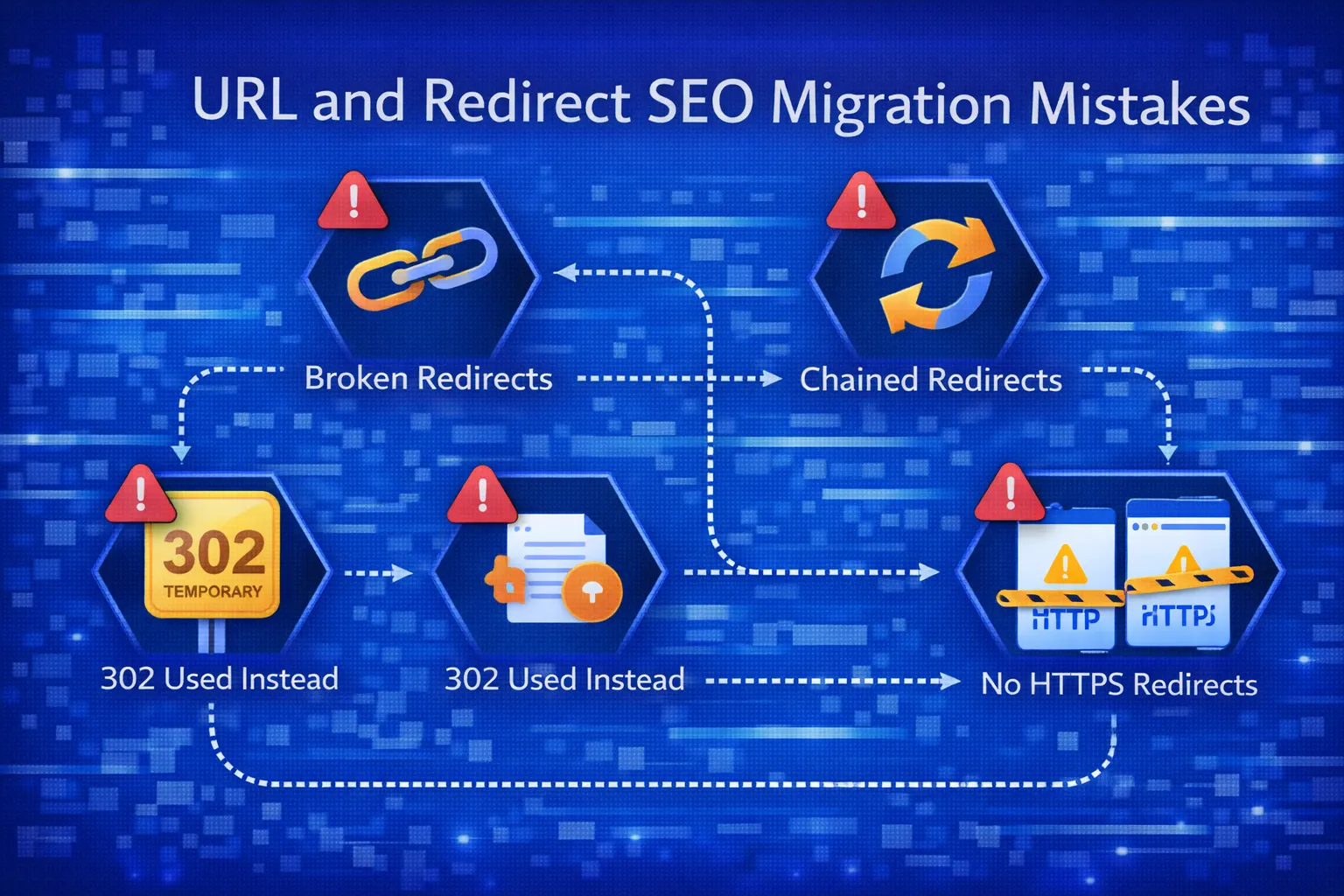
❌ Mistake #6: Missing or Incorrect 301 Redirects
Failing to implement proper 301 redirects is the #1 reason for traffic loss
during website migration.
Common redirect issues include:
- No redirects at all
- Using 302 instead of 301
- Redirecting everything to the homepage
- Broken or looping redirects
When Google hits a missing redirect, it treats the page as removed —
causing immediate ranking loss.
Fix: Every old URL must map to the most relevant new URL using a 301 redirect.
👉 Deep dive: Website Migration SEO Checklist
❌ Mistake #7: Redirect Chains and Loops
Redirect chains dilute link equity and slow down crawling.
Example of a bad chain:
/old-page → /temp-page → /new-page
Google may stop following chains after several hops, causing partial authority loss.
Fix: Redirect old URLs directly to the final destination in a single hop.
❌ Mistake #8: Changing URL Structure Without SEO Logic
Many migrations redesign URLs purely for aesthetics, ignoring search intent.
Bad example:
/services/seo-audit-92-fixes.html → /solutions/optimize-now.html
This breaks keyword relevance and confuses search engines.
SEO-friendly approach:
/blog/ecommerce-seo-audit.html → /blogs/ecommerce-seo-audit.html
Fix: Preserve keyword intent and topical relevance in URLs.
❌ Mistake #9: Canonical Tag Conflicts
Canonical mistakes silently kill rankings because Google may ignore your intended page.
Common canonical errors:
- Canonical pointing to old URLs
- Self-canonical missing
- Multiple canonicals per page
- Cross-domain canonical mistakes
Sitemap URLs must always match canonical URLs exactly.
Fix: Use one clean self-referencing canonical per page after migration.
👉 Related: Technical SEO Audit Guide
❌ Mistake #10: Forgetting to Update Internal Links
Internal links pointing to redirected URLs waste crawl budget
and weaken internal authority flow.
After migration, many sites still contain:
- Old URL references
- Redirected internal links
- Broken anchor text
Fix: Update all internal links to point directly to final URLs.
❌ Mistake #11: Pagination & Parameter Chaos
During migration, pagination and URL parameters often break:
- /page/2/ returns 404
- ?sort= parameters get indexed
- Filtered URLs create duplicates
This causes index bloat and ranking dilution.
Fix: Use canonical tags and parameter handling in Google Search Console.
❌ Mistake #12: Broken XML Sitemap URLs
Submitting old or redirected URLs in XML sitemaps sends mixed signals to Google.
Your sitemap should contain ONLY:
- 200 status URLs
- Canonical URLs
- Indexable pages
Fix: Regenerate XML sitemap post-migration and resubmit in GSC.
End of Phase 2
Phase 2 covered the most common URL and redirect-related SEO mistakes.
In Phase 3, we will dive into technical SEO, performance, indexing,
and content-related migration failures.
PHASE 3: Technical SEO, Indexing & Content Migration Mistakes
Even with perfect redirects, migrations fail if technical SEO and content integrity
are compromised. Phase 3 covers the silent SEO killers that often go
unnoticed until traffic collapses.

❌ Mistake #13: Blocking the Site with robots.txt or Noindex
One of the most catastrophic migration errors is accidentally blocking search engines.
This usually happens when staging rules are pushed live.
Common blockers include:
Disallow: / in robots.txtnoindex meta tags left active- X-Robots-Tag headers blocking indexing
Fix: Audit robots.txt, meta robots, and HTTP headers before launch.
👉 Related: Technical SEO Checklist
❌ Mistake #14: Core Web Vitals Regression
New designs often introduce heavy scripts, large images, and unoptimized fonts.
This results in worse:
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
- Interaction to Next Paint (INP)
- Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
Poor performance impacts rankings and conversions simultaneously.
Fix: Test Core Web Vitals on staging using PageSpeed Insights and Lighthouse.
❌ Mistake #15: Losing or Changing High-Performing Content
During redesigns, content is often rewritten, shortened, or removed.
This leads to immediate ranking loss for established keywords.
High-risk changes include:
- Removing sections with ranking keywords
- Changing heading structure (H1–H3)
- Deleting internal links
Fix: Preserve core content during migration. Optimize only after rankings stabilize.
❌ Mistake #16: Duplicate Content After Migration
Migration often creates duplicate URLs unintentionally:
- HTTP vs HTTPS
- WWW vs non-WWW
- Trailing slash variations
- Parameter-based duplicates
Duplicate content dilutes ranking signals and confuses Google.
Fix: Enforce one URL version using canonicals and redirects.
❌ Mistake #17: Missing or Broken Structured Data
Schema markup often breaks during migration, especially when templates change.
This can result in:
- Loss of rich results
- Lower CTR
- Schema validation errors
Fix: Validate structured data using Google Rich Results Test after launch.
❌ Mistake #18: Analytics & Conversion Tracking Failures
SEO performance cannot be measured if tracking breaks.
Common tracking issues include:
- GA4 not firing
- GSC not verified
- Conversion events missing
This creates blind spots that delay issue detection.
Fix: Validate GA4, GSC, and event tracking on staging before launch.
❌ Mistake #19: Forgetting Image SEO During Migration
Image assets are often replaced or renamed during migration.
This causes:
- Broken image links
- Lost image search traffic
- Slower page load
Fix: Preserve image filenames, alt text, and compression.
❌ Mistake #20: JavaScript Rendering Issues
Modern sites rely heavily on JavaScript, which Google may not render immediately.
Migration often introduces:
- Content hidden behind JS
- Delayed rendering
- Indexing gaps
Fix: Ensure critical content is server-rendered or HTML-first.
End of Phase 3
Phase 3 covered the most common technical and content-related SEO migration mistakes.
In Phase 4, we will focus on post-migration monitoring, recovery actions,
FAQs, and final SEO checklists.
PHASE 4: Post-Migration SEO Monitoring & Recovery
Launching a website migration is not the finish line — it is the starting point.
Most ranking drops happen after launch due to poor monitoring,
delayed fixes, or ignored SEO signals.
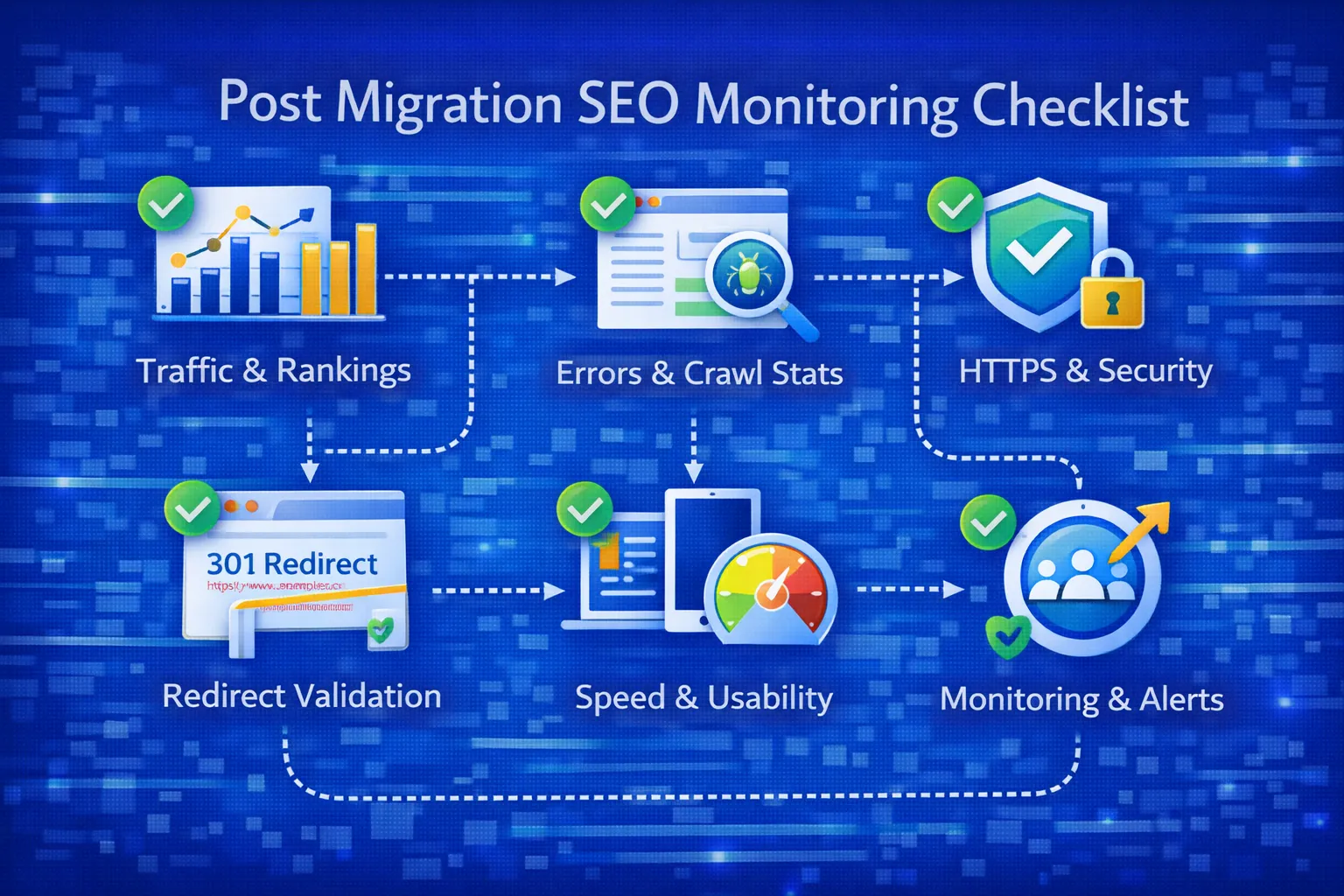
❌ Mistake #21: Not Monitoring Google Search Console Daily
Search Console is the first place Google reports problems.
Ignoring it after migration delays recovery.
- Coverage errors
- Page indexing issues
- Enhancement & schema warnings
Fix: Monitor GSC daily for at least 30 days post-migration.
❌ Mistake #22: Ignoring Crawl Stats & Server Logs
Crawling patterns change after migration.
Without log analysis, critical URLs may be ignored by search engines.
Fix: Review server logs to confirm Googlebot is crawling key pages.
❌ Mistake #23: Delayed Redirect Fixes
Broken or misfiring redirects should be fixed immediately.
Waiting weeks compounds ranking loss.
Fix: Resolve redirect issues within 24–72 hours.
❌ Mistake #24: Not Updating Internal Links Post-Launch
Internal links often still point to old URLs.
This wastes crawl budget and weakens link equity.
Fix: Update internal links to point directly to final URLs.
❌ Mistake #25: Panic Changes After Ranking Fluctuations
Temporary volatility is normal after migration.
Drastic changes too early often make things worse.
Fix: Allow 2–4 weeks before making major SEO changes.
❌ Mistake #26: Not Submitting Updated Sitemap
Google relies on sitemaps to discover new URLs efficiently.
Old sitemaps slow down re-indexing.
Fix: Submit the new XML sitemap immediately after launch.
❌ Mistake #27: Forgetting External Link Updates
High-authority backlinks pointing to old URLs lose value.
Fix: Contact top linking domains and request URL updates.
❌ Mistake #28: No SEO Recovery Plan
Many teams hope rankings will return automatically.
Without a recovery plan, issues linger for months.
Fix: Create a 30-60-90 day SEO recovery roadmap.
SEO Migration Mistakes – Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is website migration in SEO?
Website migration in SEO refers to major changes like domain, platform, URL structure, or design that can impact search rankings and organic traffic.
2. Why does SEO matter during website migration?
SEO ensures rankings, backlinks, and indexed pages are preserved during migration, preventing traffic loss.
3. Can website migration hurt rankings?
Yes, improper redirects, indexing issues, or content removal can cause ranking drops.
4. How long does SEO recovery take after migration?
SEO recovery usually takes 2–8 weeks depending on site size, crawl rate, and migration quality.
5. Are 301 redirects mandatory during migration?
Yes, 301 redirects transfer link equity and signal permanent URL changes to search engines.
6. What happens if I skip redirects?
Skipping redirects causes broken links, lost authority, and severe ranking drops.
7. Should I migrate content during redesign?
Yes, all valuable content should be migrated to maintain keyword relevance and rankings.
8. Can I change content during migration?
Major content changes should be postponed until rankings stabilize post-migration.
9. How do I protect backlinks during migration?
Map old URLs to new ones using 301 redirects and update high-value backlinks manually.
10. What tools are best for SEO migration?
Google Search Console, Screaming Frog, Ahrefs, and server log analyzers are essential.
11. Should staging sites be indexed?
No, staging sites should be blocked using noindex or authentication.
12. What is the biggest SEO migration mistake?
Forgetting redirects and blocking search engines accidentally are the most damaging mistakes.
13. How important is sitemap submission after migration?
Submitting an updated sitemap accelerates re-indexing of new URLs.
14. Does site speed affect migration SEO?
Yes, slower pages reduce crawl efficiency and rankings.
15. Should internal links be updated after migration?
Yes, all internal links should point directly to final URLs.
16. How does migration affect Google Ads?
Broken URLs and slow pages can lower Quality Score and cause ad disapprovals.
17. Can HTTPS migration affect SEO?
Yes, HTTPS migration requires proper redirects and certificate validation.
18. Is domain migration risky?
Domain migration carries higher risk but is safe when redirects and signals are preserved.
19. How do I monitor SEO after migration?
Track rankings, crawl errors, coverage reports, and server logs daily.
20. Should canonical tags be updated?
Yes, canonicals must point to new URLs to avoid duplication.
21. How long should redirects remain active?
Redirects should remain active for at least 12 months.
22. Can migration improve SEO?
Yes, when combined with performance, UX, and technical improvements.
23. What is crawl budget during migration?
Crawl budget refers to how often search engines crawl your pages post-migration.
24. Should robots.txt be checked after migration?
Yes, incorrect rules can block important pages.
25. Is schema markup affected during migration?
Yes, schema must be validated and re-tested after migration.
26. Can JavaScript frameworks impact migration SEO?
Yes, improper rendering can prevent indexing.
27. Should I pause publishing during migration?
Pausing content publishing reduces indexing confusion.
28. How do I handle pagination during migration?
Pagination URLs must be redirected and indexed properly.
29. Is log file analysis necessary?
Yes, it confirms how search engines crawl your new site.
30. Do I need an SEO migration checklist?
Yes, a checklist prevents missed steps and costly SEO losses.
About the Author
Written by Hassan, SEO Consultant at
DigitalSkillEarnHub.
Hassan has 5+ years of hands-on experience in technical SEO,
large-scale website migrations, enterprise-level redirect strategies,
and post-migration recovery.
This guide is based on real client migrations, production environments,
and Google-compliant best practices. The goal is to help businesses,
freelancers, and professionals migrate websites safely without losing
rankings, traffic, or revenue.
Conclusion: How to Migrate a Website Without Losing Rankings
Website migration SEO is not about shortcuts — it is about precision.
When done correctly, migration can improve performance,
scalability, and long-term growth.
By following all four phases of this guide, you protect your
rankings, traffic, and revenue while setting your website up
for future success.
If you are planning a migration and want zero SEO risk,
professional planning and execution make all the difference.
Website Migration SEO – Topic Cluster Plan
This pillar guide is supported by a structured topic cluster to improve
topical authority, internal linking, and organic visibility across related
SEO migration subjects.
| Cluster Type |
Article Title |
Internal Link Anchor |
| Pillar |
Website Migration SEO: Complete Guide (2026) |
Website Migration SEO Guide |
| Supporting |
Website Migration SEO Checklist
|
SEO migration checklist |
| Supporting |
Common SEO Migration Mistakes to Avoid |
SEO migration mistakes |
| Supporting |
Technical SEO Audit Checklist |
technical SEO audit |
| Supporting |
301 Redirect Strategy for SEO |
301 redirect strategy |
| Supporting |
Post-Migration SEO Monitoring Guide |
post-migration SEO |
Google Ads Compliance & Content Transparency
This article is published for educational and informational purposes only.
It does not provide guarantees regarding search rankings, traffic growth,
advertising performance, or revenue outcomes.
All SEO strategies, migration steps, tools, and examples discussed are based
on industry best practices and real-world experience. Results may vary
depending on website condition, competition, implementation quality, and
search engine updates.
DigitalSkillEarnHub complies with Google Ads content policies by avoiding
misleading claims, prohibited practices, and unverifiable promises.
No black-hat techniques, policy violations, or deceptive methods are promoted.




