301 Redirect Strategy for SEO: The Complete Guide (2026)
A poorly implemented redirect strategy is one of the biggest reasons websites lose traffic, rankings, and revenue during migrations. This guide explains exactly how to plan, implement, test, and monitor 301 redirects the right way — without triggering SEO disasters.
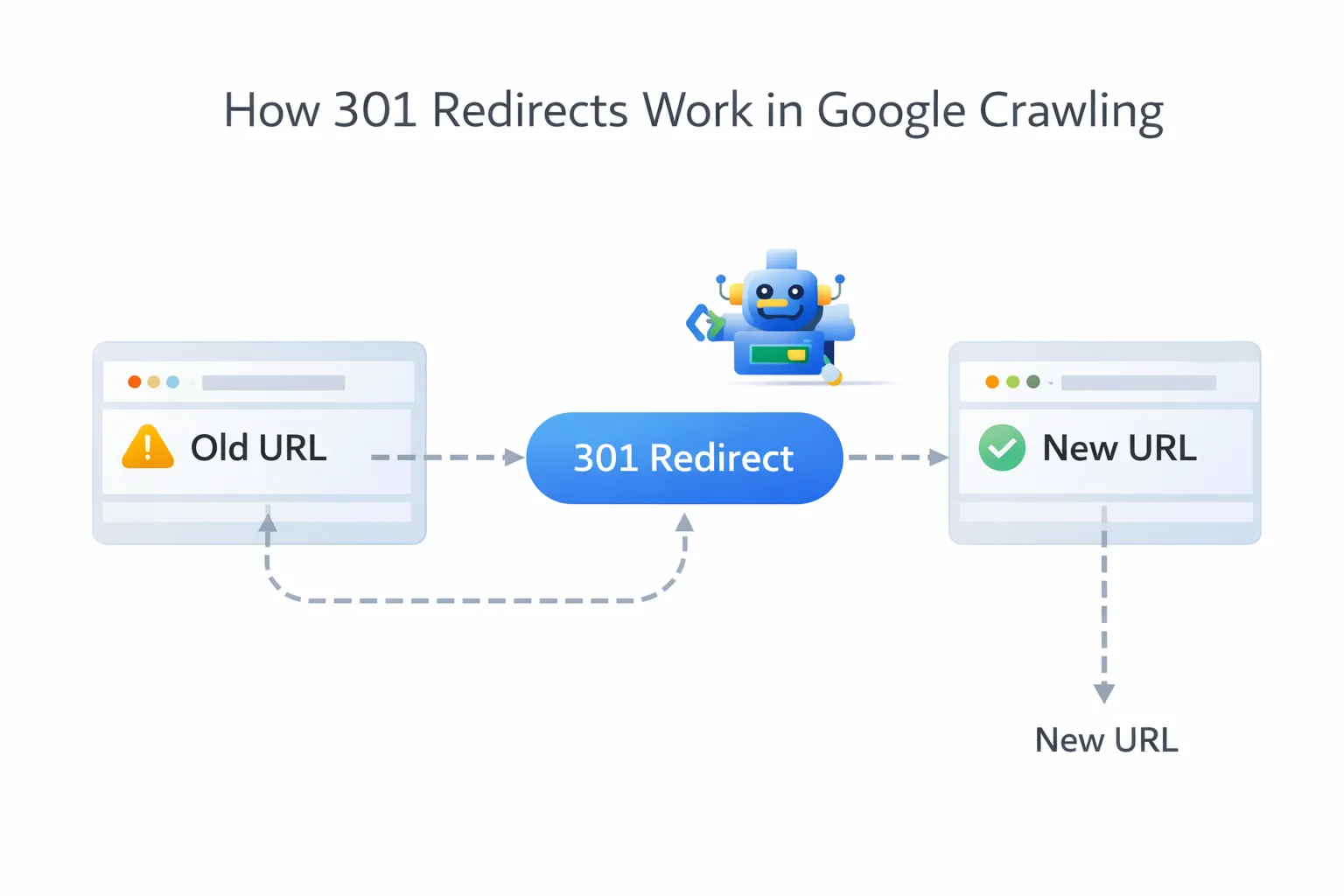
What Is a 301 Redirect?
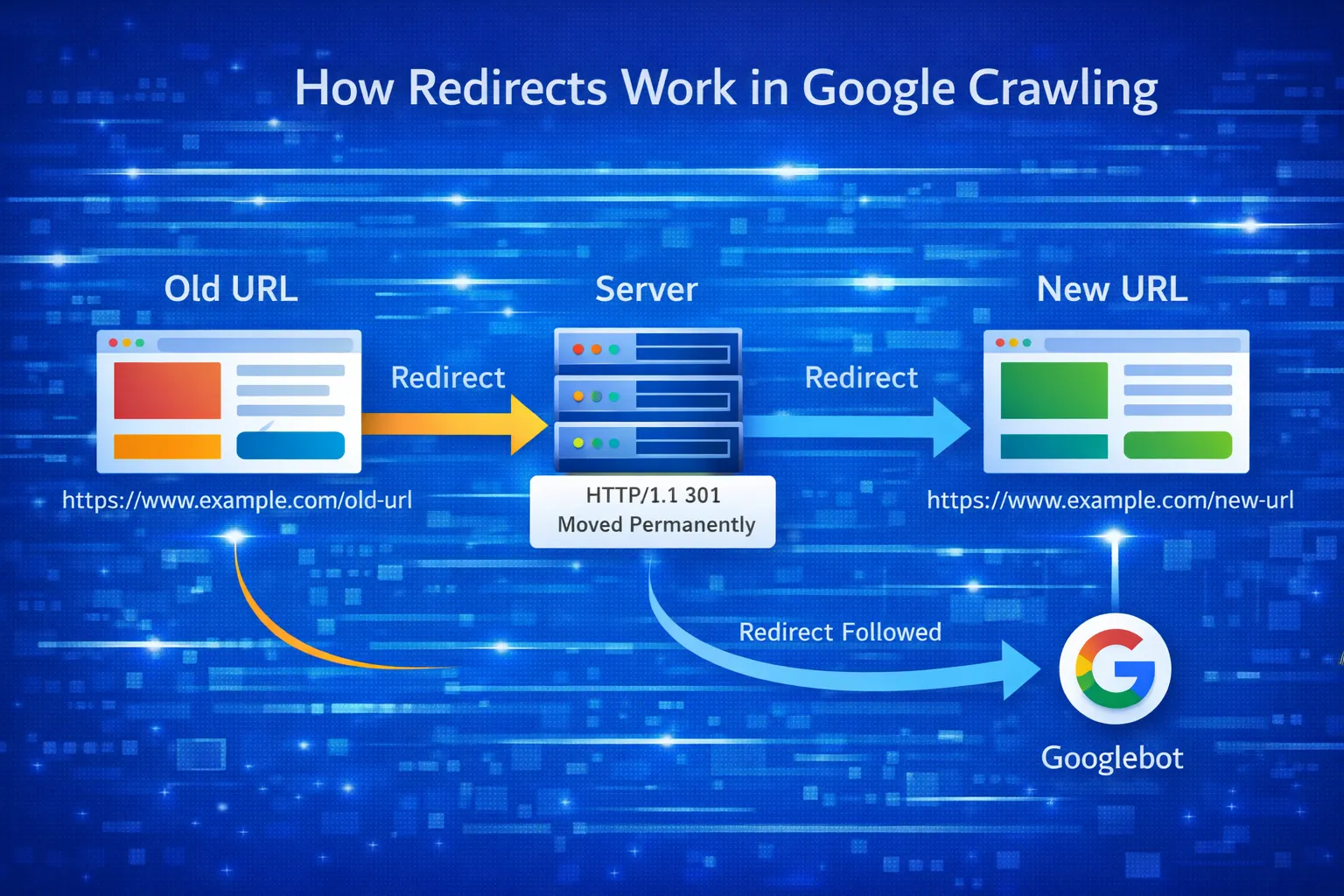
A 301 redirect is a permanent HTTP status code that tells search engines and browsers that a page has moved permanently to a new URL.
From an SEO perspective, 301 redirects are essential because they:
- Transfer ranking signals
- Preserve backlinks
- Prevent duplicate content
- Maintain crawl efficiency
Why 301 Redirects Are Critical for SEO
Search engines treat URLs as unique entities. If you change URLs without redirects, Google treats the new page as brand new — meaning:
- Rankings reset
- Backlinks lose value
- Traffic drops instantly
A proper website migration SEO checklist always starts with redirect planning.
When You Must Use 301 Redirects

- Website migrations
- Domain changes
- HTTP → HTTPS
- URL structure updates
- Deleted or merged pages
301 vs 302 Redirects: SEO Difference
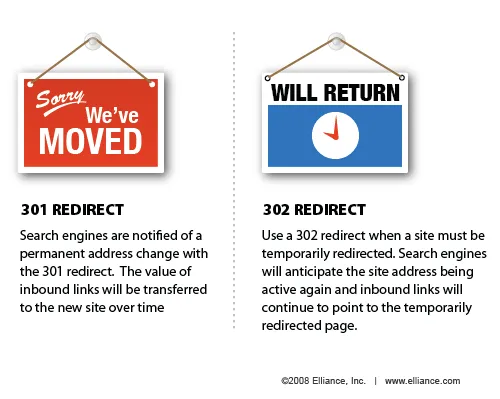
| 301 Redirect | 302 Redirect |
|---|---|
| Permanent | Temporary |
| Transfers SEO equity | Does NOT fully transfer equity |
| Used for migrations | Used for short-term testing |
How to Create a Redirect Mapping Sheet
Before implementation, you must create a redirect map.
| Old URL | New URL | Status |
|---|---|---|
| /old-page.html | /new-page.html | 301 |
This step alone prevents 80% of migration SEO failures.
301 Redirects During Website Migration

During migration, redirects should:
- Be one-to-one
- Avoid redirect chains
- Point to the most relevant page
Avoid the mistakes covered in SEO migration mistakes to avoid.
How to Implement 301 Redirects
Apache (.htaccess)
Redirect 301 /old-page.html https://example.com/new-page.html
Nginx
rewrite ^/old-page.html$ https://example.com/new-page.html permanent;
CMS Level
- WordPress: RankMath / Redirection
- Shopify: URL Redirects
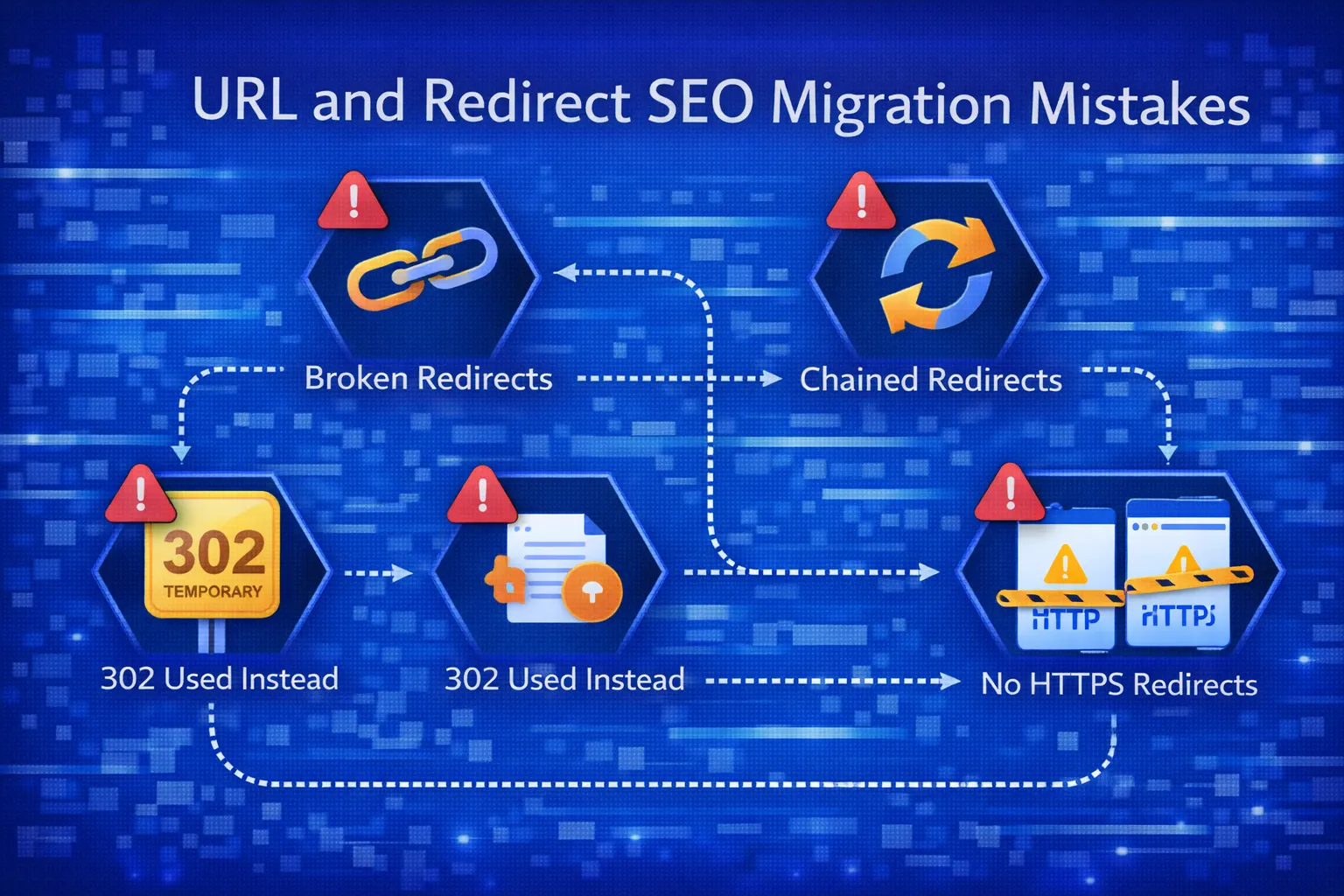
Common 301 Redirect Mistakes

- Redirecting everything to homepage
- Redirect chains
- Redirect loops
- Blocking redirected URLs in robots.txt
How to Test 301 Redirects
- Google Search Console
- Screaming Frog
- curl / browser dev tools
Post-Migration Redirect Monitoring
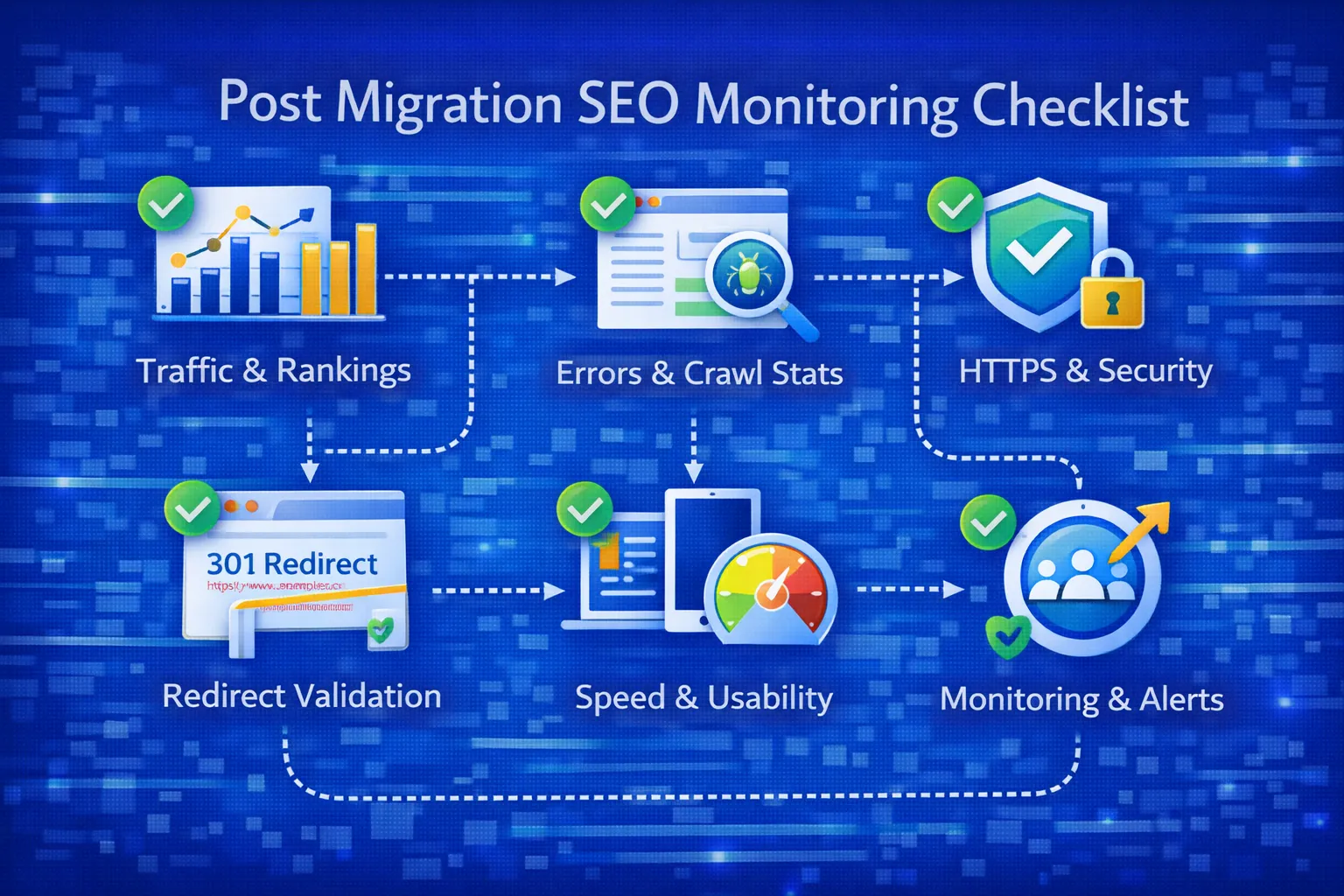
After launch:
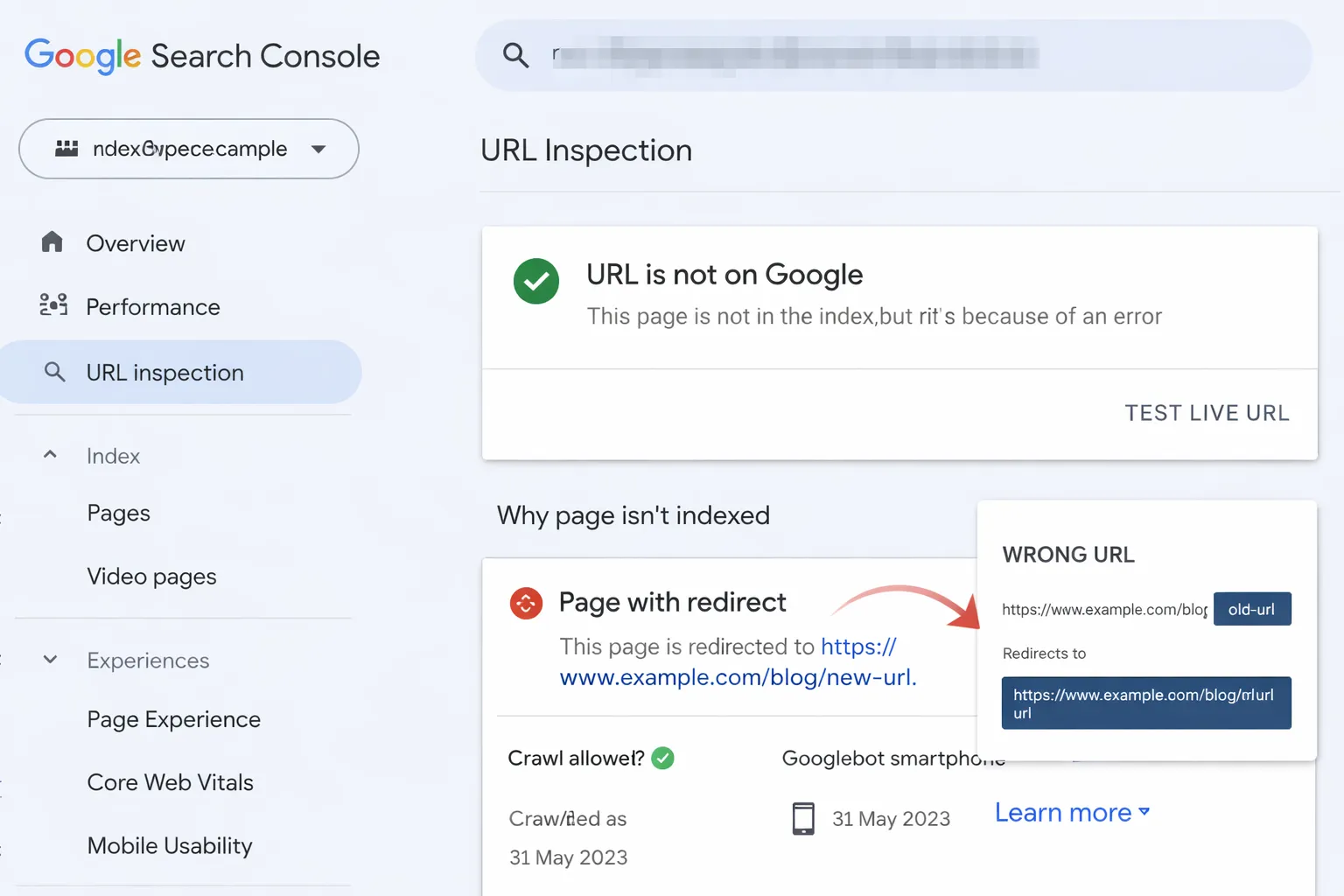
- Check Coverage reports
- Monitor “Page with redirect”
- Fix 404 errors immediately
If you see issues, refer to Page with Redirect in Google Search Console.
Final Thoughts: Build Redirects Once, Protect Rankings Forever
A 301 redirect strategy is not just a technical task — it is a ranking protection system. When implemented correctly, it preserves organic traffic, backlink equity, crawl efficiency, and user experience during migrations, URL changes, and site restructures.
The most successful SEO migrations follow a simple rule: every old URL must have a clear, relevant destination. This guide has shown you how to plan redirect mapping, avoid chains and loops, implement server-side redirects, test them properly, and monitor performance after launch.
Whether you are migrating a small blog or a large enterprise website, a clean 301 redirect strategy ensures Google understands your changes without resetting your SEO progress.
If you are preparing for a migration, make sure this guide is used alongside a complete website migration SEO checklist and a full SEO audit to eliminate risk.
Done right, redirects don’t lose rankings — bad planning does.
Planning a Website Migration?
If you are preparing for a website migration, URL restructuring, or HTTPS move, a clean 301 redirect strategy is only one part of the process.
Use this guide together with a complete Website Migration SEO Checklist and a detailed Technical SEO Audit to avoid ranking loss.
Need a second opinion before launch? Explore our SEO services or review real migration case studies in our SEO blog.
Frequently Asked Questions About 301 Redirect Strategy for SEO
1. What is a 301 redirect in SEO?
A 301 redirect is a permanent redirect that tells search engines a URL has permanently moved to a new location. It passes most ranking signals and link equity from the old URL to the new one.
2. Do 301 redirects affect SEO rankings?
Yes, but positively when implemented correctly. A proper 301 redirect helps preserve rankings, backlinks, and crawl equity during URL changes or site migrations.
3. How much SEO value does a 301 redirect pass?
Google has confirmed that modern 301 redirects pass nearly 100% of link equity, as long as redirects are clean, direct, and relevant.
4. When should I use a 301 redirect?
Use a 301 redirect when changing URLs, migrating domains, merging pages, switching CMS platforms, or permanently removing content.
5. What happens if I don’t use 301 redirects during migration?
Without redirects, search engines treat new URLs as brand-new pages, causing ranking loss, traffic drops, and lost backlink value.
6. Are 301 redirects better than 302 redirects for SEO?
Yes. A 301 redirect is permanent and passes ranking signals, while a 302 redirect is temporary and should only be used for short-term changes.
7. Can too many 301 redirects hurt SEO?
Excessive redirects can slow crawl efficiency and create redirect chains, which negatively impact SEO and user experience.
8. What is a redirect chain?
A redirect chain occurs when one URL redirects to another, which then redirects again. Chains dilute link equity and should be replaced with single-step redirects.
9. What is a redirect loop?
A redirect loop happens when URLs redirect back to each other endlessly, preventing pages from loading and blocking search engine crawling.
10. Should every old URL be redirected?
Yes, every valuable indexed URL should redirect to the most relevant new page to preserve rankings and avoid 404 errors.
11. Is it okay to redirect all pages to the homepage?
No. Redirecting unrelated pages to the homepage is considered a soft 404 and can harm SEO. Always redirect page-to-page contextually.
12. How do I create a redirect map?
A redirect map is created by exporting all old URLs and mapping them one-to-one with their most relevant new URLs before migration.
13. How long does Google take to process 301 redirects?
Google typically processes 301 redirects within days to weeks, depending on crawl frequency, site size, and internal linking.
14. Should redirected URLs remain in the XML sitemap?
No. XML sitemaps should only contain final destination URLs, not redirected or non-indexable pages.
15. Should I block redirected URLs in robots.txt?
No. Redirected URLs must remain crawlable so search engines can pass signals to the new destination pages.
16. Do 301 redirects need canonical tags?
No. A properly implemented 301 redirect removes the need for canonicals because it clearly signals the preferred URL.
17. Do 301 redirects slow down a website?
A few redirects are fine, but excessive or chained redirects increase server requests and can impact performance and Core Web Vitals.
18. How do 301 redirects affect backlinks?
When done correctly, 301 redirects transfer backlink equity from old URLs to new URLs, preserving authority and rankings.
19. How long should I keep 301 redirects live?
Keep redirects active for at least 12–18 months, or permanently if the URL will never be reused.
20. Can I remove 301 redirects later?
Redirects can be removed only after search engines fully process the changes, traffic stabilizes, and backlinks are updated.
21. How do I implement 301 redirects in .htaccess?
Use server-level rewrite rules in the .htaccess file to create permanent redirects for Apache-based servers.
22. How do I set up 301 redirects in WordPress?
WordPress redirects can be managed using plugins or server-level rules, but server-side redirects are always preferred for SEO.
23. How do I test if redirects are working?
Redirects can be tested using browser tools, SEO crawlers, or Google Search Console URL Inspection.
24. Why does Google show “Page with redirect” in Search Console?
This is informational, not an error. It means Google found a redirect and is indexing the destination URL instead.
25. Should I fix “Page with redirect” in GSC?
No fix is required unless the redirect is incorrect, broken, or pointing to an irrelevant page.
26. Do redirects affect crawl budget?
Yes. Excessive redirects waste crawl budget, especially on large sites, making clean redirect strategy essential.
27. Can redirects cause traffic drops?
Poorly implemented redirects can cause ranking loss and traffic drops, especially when redirect relevance is ignored.
28. Should I redirect deleted pages?
If a deleted page had traffic or backlinks, redirect it to the closest relevant page instead of returning a 404.
29. Do 301 redirects impact Core Web Vitals?
Redirects add loading steps, which can increase LCP and TTFB if not minimized.
30. How do I audit existing redirects?
Redirect audits involve crawling the site, identifying chains, loops, non-200 destinations, and mapping fixes.
31. Can redirects affect mobile SEO?
Yes. Incorrect mobile redirects can cause indexing issues and poor user experience on mobile devices.
32. Should HTTPS migration use 301 redirects?
Yes. HTTP to HTTPS migrations must use 301 redirects to preserve rankings and ensure secure indexing.
33. Are JavaScript redirects bad for SEO?
JavaScript redirects are less reliable than server-side 301 redirects and should be avoided for SEO-critical migrations.
34. Do 301 redirects work for international SEO?
Yes, but they must be combined with proper hreflang and regional targeting strategies.
35. What is the biggest 301 redirect mistake?
Redirecting all pages to the homepage instead of maintaining contextual relevance.
36. Can redirects help consolidate duplicate pages?
Yes. Redirects are an effective way to merge duplicate or thin content into a stronger canonical page.
37. Should pagination URLs be redirected?
No. Pagination URLs should usually remain indexable and not redirected unless they are deprecated.
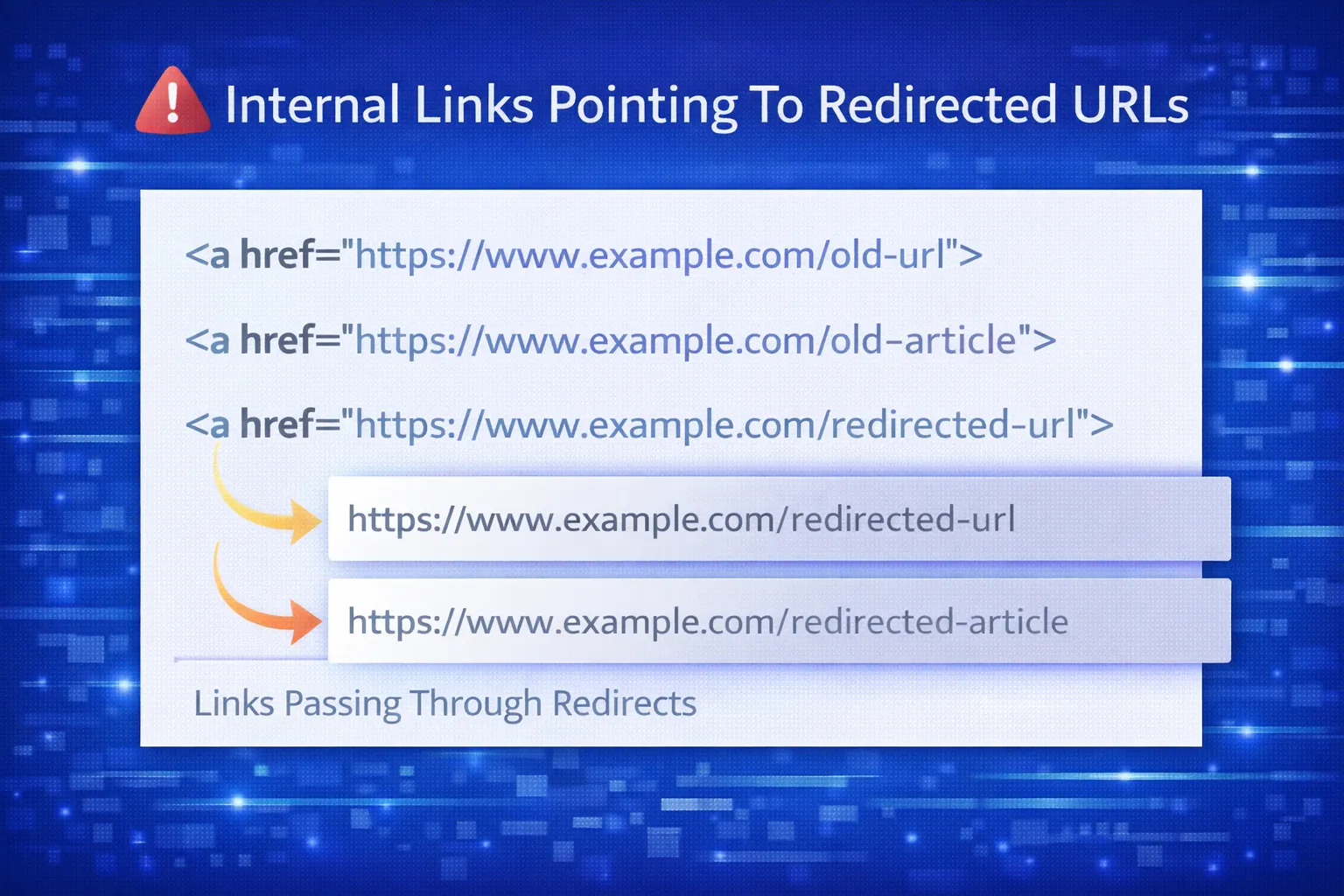
38. How do redirects affect internal linking?
Internal links should always point directly to final URLs, not redirected ones, to preserve crawl efficiency.
39. Can redirects fix broken links?
Yes. Redirects can recover value from broken URLs caused by deleted or changed pages.
40. What is the best 301 redirect strategy for SEO?
The best strategy is one-to-one URL mapping, server-side redirects, zero chains, clean sitemaps, and continuous monitoring post-migration.
