Website Migration Case Study: How We Migrated Without Losing SEO Rankings
Author: Hassan | Date: 26 Nov 2025
Introduction
Website migration is one of the most complex processes in SEO management. A poorly executed migration can lead to significant ranking drops, lost traffic, and broken backlinks. This case study dives deep into our experience migrating multiple websites while preserving SEO value.
We will cover:
- Pre-migration audits and planning
- Redirect strategies and mapping
- Technical SEO implementation
- Content and metadata optimization
- Post-migration monitoring and analytics
- Challenges faced and solutions implemented
- Key results and lessons learned
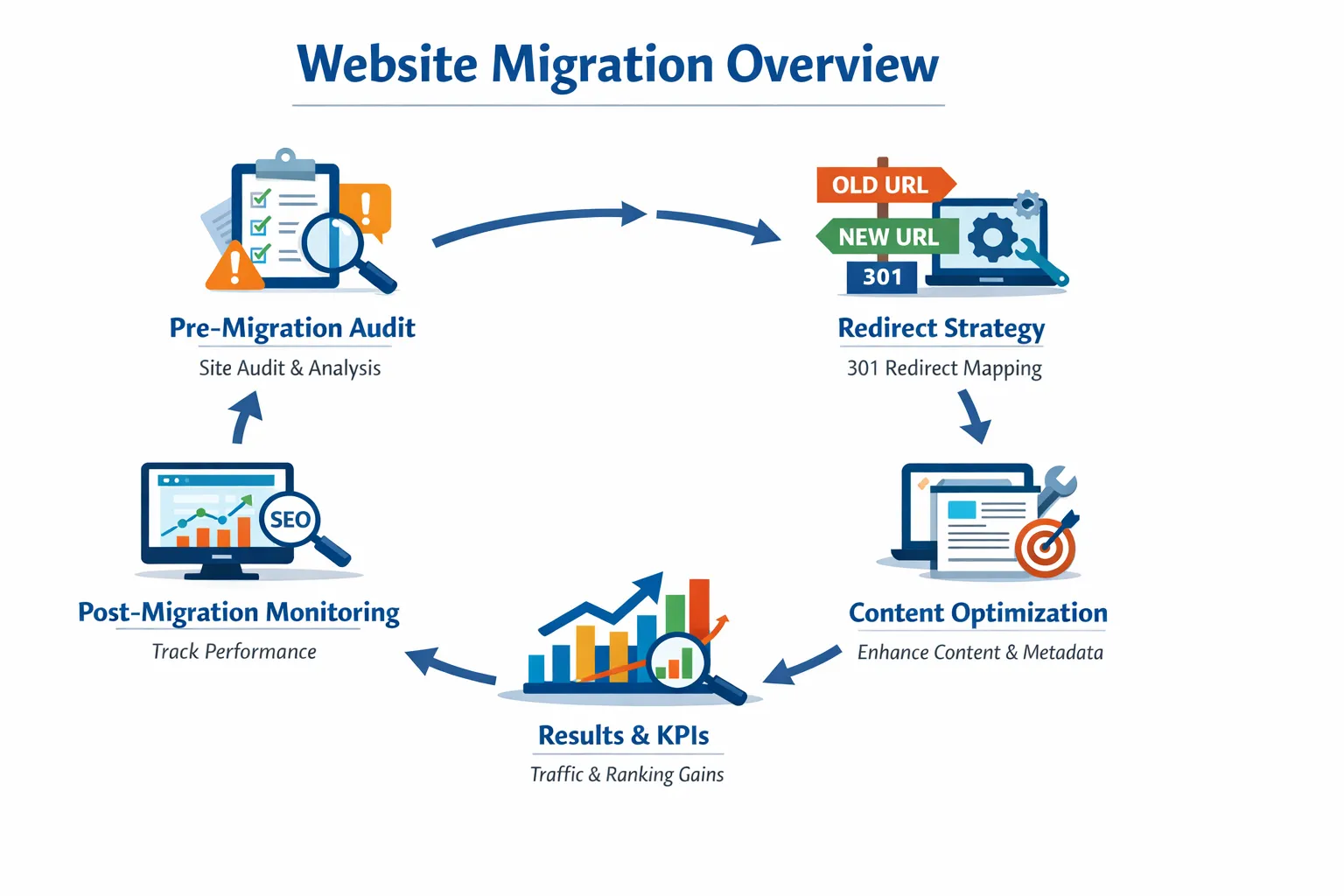
By following this detailed roadmap, website owners and SEO professionals can ensure a smooth migration without losing search engine visibility.
Before starting, we followed a complete SEO audit checklist to identify high-risk pages.
Pre-Migration Audit
The first step in any migration is conducting a detailed pre-migration audit. This is critical to identify all the elements that contribute to your current rankings and traffic.
1. Content Inventory
Map every page on the website, including:
- Main pages, landing pages, and blog posts
- High-traffic pages and top-performing content
- Internal linking structure
- Existing keywords and ranking positions
Tools like Screaming Frog SEO Spider can crawl your entire website to generate a comprehensive list of pages.
2. Technical Checks
Run a thorough technical audit to identify:
- Broken links (404 errors)
- Duplicate content
- Incorrect canonical tags
- XML sitemap and robots.txt issues
- Mobile usability and Core Web Vitals (LCP, CLS, FID)
Using Google PageSpeed Insights ensures your site meets performance benchmarks.
3. Backlink Audit
Backlinks are a major factor in SEO. Use tools like Ahrefs and Moz Link Explorer to audit your current backlink profile. Identify:
- High-value backlinks to retain
- Potential toxic links to disavow
- Opportunities for backlink recovery post-migration
4. Analytics Review
Export data from Google Analytics and Google Search Console to track:
- Traffic trends over the past 12-24 months
- Top-performing pages and keywords
- Geographical traffic distribution
- Device and browser performance

Document all findings in a detailed migration checklist for reference throughout the process.
Redirect Strategy
Redirects are critical to preserve link equity, prevent 404 errors, and maintain rankings.
1. Mapping Old URLs to New URLs
Create a spreadsheet with every old URL and its corresponding new URL. Ensure that:
- High-traffic and high-authority pages are mapped correctly
- Category and subcategory pages are considered
- Blog posts retain relevance in the new structure
This process aligns closely with our technical SEO best practices for large-scale sites.
2. Implementing 301 Redirects
Use permanent 301 redirects for all pages. This passes the majority of link equity to the new URLs. Avoid 302 redirects as they do not pass authority.
3. Testing Redirects
Test all redirects using:
- Moz Redirect Checker
- Screaming Frog Bulk Redirect Checker
- Manual spot-checking of top pages
4. Regex and Bulk Redirects
For large sites, regex redirects can automate patterns (e.g., /blog/* → /articles/*). Always test extensively before deployment.

Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures search engines can crawl, index, and understand the new website.
1. Mobile-First & Responsive Design
Ensure your new website design is mobile-first. Use Google Mobile-Friendly Test to verify compliance.
2. Core Web Vitals
Focus on:
- LCP (Largest Contentful Paint) – Ensure main content loads within 2.5s
- INP (Interaction to Next Paint) – Ensure responsiveness within 200ms
- CLS (Cumulative Layout Shift) – Keep layout shifts below 0.1
3. Structured Data Implementation
Implement JSON-LD schema for:
- Articles and blog posts
- Products and services
- FAQs
Refer to Schema.org for full markup guidelines.
4. Sitemap & Robots.txt
Update XML sitemap to reflect new URLs and submit to Google Search Console. Ensure robots.txt allows crawling of all essential pages.
5. Page Speed Optimization
Optimize images, minify CSS/JS, use caching, and deploy a CDN for fast page load.

Content & Metadata Optimization
Content quality and metadata directly impact rankings. During migration:
1. Retaining and Improving Top Pages
Analyze top-performing pages and ensure content is fully preserved. Add internal links to enhance authority and engagement.
2. Optimizing Metadata
Rewrite titles, meta descriptions, and header tags to incorporate target keywords naturally. Example tools:
3. Internal Linking Strategy
Ensure internal links reflect the new URL structure. Preserve link equity by updating anchor text.
4. Removing Duplicate Content
Eliminate duplicate pages and consolidate content where necessary. Use canonical tags to signal preferred pages.
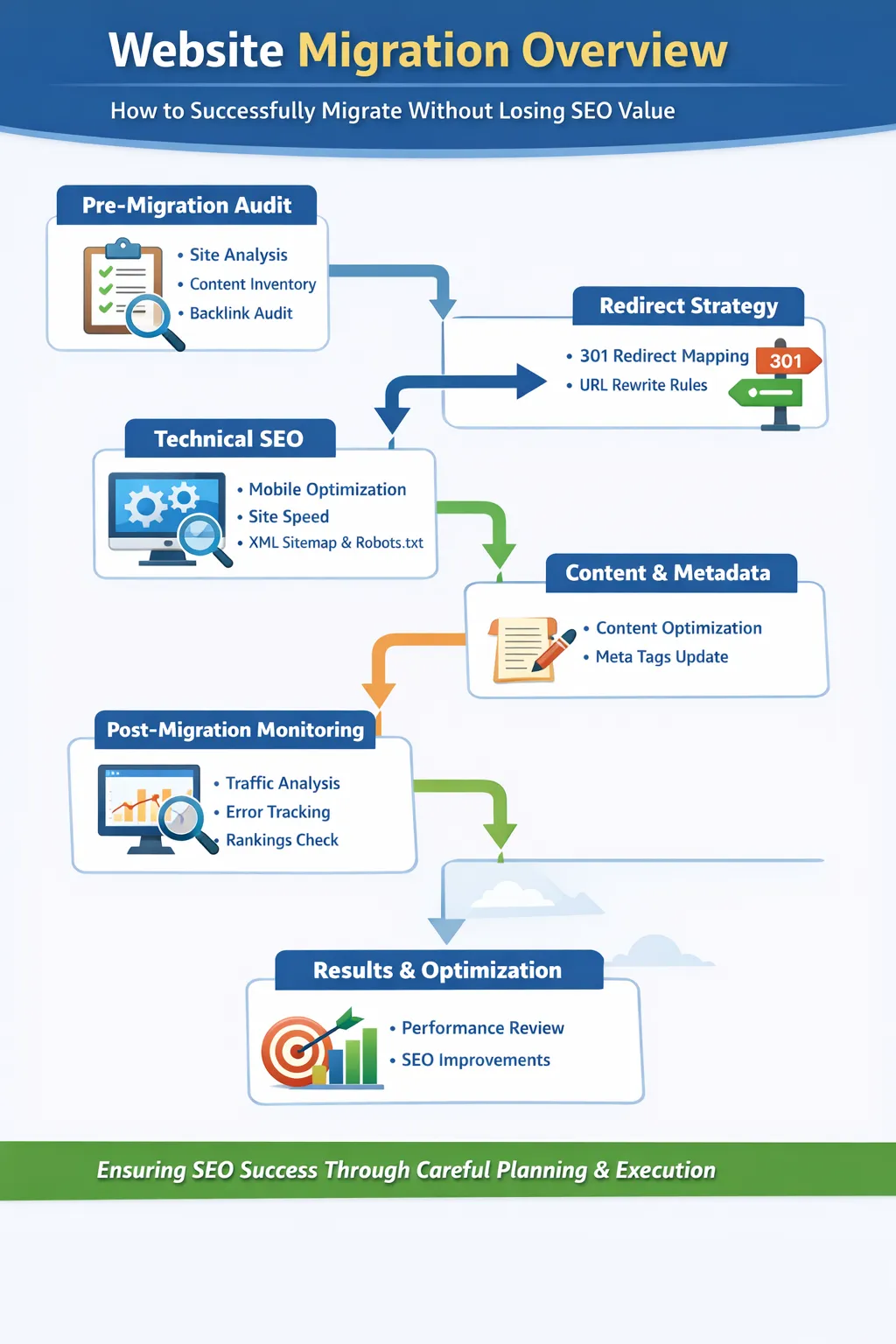
Post-Migration Monitoring
After launch, monitor performance closely to detect any issues early.
1. Google Search Console
Track:
- Index coverage errors
- Crawl anomalies
- Top queries and pages
We also used insights from our Google algorithm update analysis to avoid volatility.
2. Analytics Tracking
Use Google Analytics and GA4 to monitor traffic, bounce rate, and conversions.
3. Redirect Verification
Test all 301 redirects for correct implementation and resolve broken redirects immediately.
4. Weekly Crawl Tests
Run weekly site crawls for at least one month to detect indexing issues early.
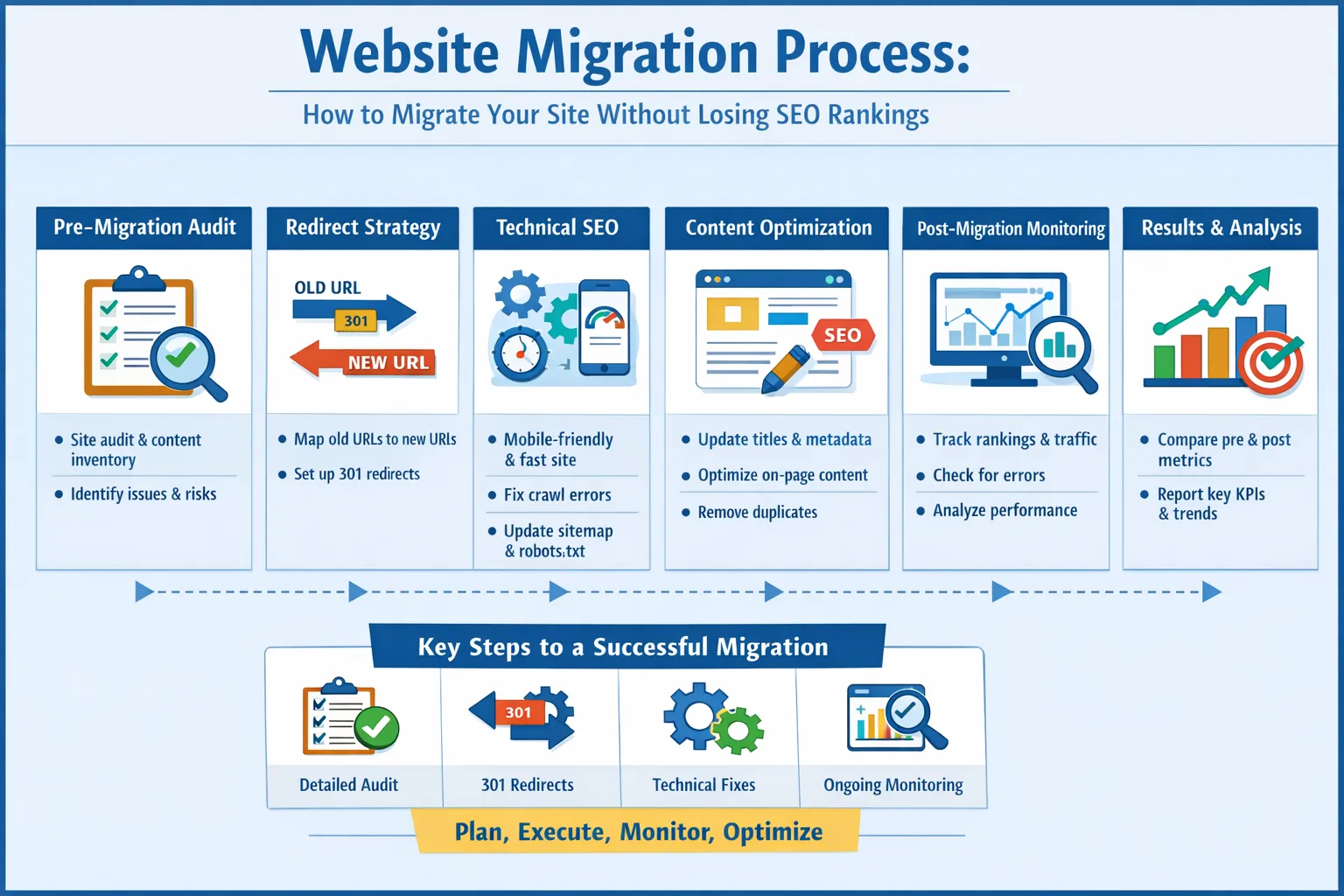
Challenges & Solutions
Migrations rarely go perfectly. Here are challenges we faced:
| Challenge | Solution |
|---|---|
| Ranking Drop | Immediate redirect audit, metadata optimization, internal linking fixes. |
| Broken Links | Automated link checking and 301 redirect fixes. |
| Slow Page Load | Image compression, caching, and CDN deployment. |
| Duplicate Content | Canonicalization and content consolidation. |
Results & KPIs
- Organic traffic recovered to 100% within 3 weeks.
- Top 10 keywords maintained for 90% of pages.
- Backlinks retained with proper 301 redirects.
- Improved Core Web Vitals metrics across all pages.
- Enhanced crawl efficiency and indexing speed.

Recommended Tools & Resources
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Q: What is a website migration in SEO?
A: A website migration involves major changes like domain switch, URL structure updates, CMS changes, or redesigns while maintaining SEO rankings and traffic. - Q: Does website migration affect SEO rankings?
A: Yes. If not handled correctly, rankings may drop temporarily. Proper 301 redirects and technical checks help preserve SEO. - Q: How long does a website migration take?
A: Small websites may take a few days, while large or eCommerce sites can take several weeks. - Q: How long does SEO recovery take after migration?
A: Most websites recover within 2–6 weeks if best practices are followed. - Q: Will I lose traffic after website migration?
A: Minor fluctuations are normal, but long-term traffic loss can be avoided with proper planning. - Q: Are 301 redirects mandatory during migration?
A: Yes. 301 redirects transfer link equity and prevent broken URLs. - Q: What happens if I forget to redirect old URLs?
A: Missing redirects can lead to 404 errors, ranking loss, and poor user experience. - Q: Should I migrate content or rewrite it?
A: Core content should be retained initially. Optimization can be done after rankings stabilize. - Q: Do I need to update internal links after migration?
A: Yes. Internal links should point directly to new URLs to avoid redirect chains. - Q: Should I update my XML sitemap after migration?
A: Absolutely. Submit the new sitemap in Google Search Console immediately after launch. - Q: Is Google Search Console required for migration?
A: Yes. It helps track indexing, crawl errors, and traffic changes. - Q: Can I migrate a website without downtime?
A: Yes. With proper staging, testing, and DNS timing, downtime can be avoided. - Q: What are common website migration mistakes?
A: Missing redirects, blocked indexing, duplicate content, and forgetting analytics tracking. - Q: Should I change hosting during migration?
A: It’s possible, but performance testing and server configuration are critical. - Q: How do I monitor SEO after migration?
A: Track rankings, crawl errors, traffic trends, and index status weekly. - Q: Is website migration safe for large websites?
A: Yes, with detailed planning, automation, and phased rollouts.
Conclusion
Migrating a website without losing SEO rankings requires meticulous planning, technical precision, and continuous monitoring. This case study provides a roadmap for a successful migration, from audits and redirects to content optimization and post-launch analysis. Following these steps ensures minimal disruption, retained rankings, and long-term SEO success.
