Crawled – Currently Not Indexed: Meaning, Causes & Fix Strategy (2026)
Updated: 2026-01-26 · By Hassan · Technical SEO Series (Part 1 of 4)
- What Does “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
- How Google Indexing Actually Works
- Why Google Crawls Pages But Doesn't Index Them
- Top Root Causes (New & Established Sites)
- SEO Fundamentals You Must Fix First
- Quick Self Diagnosis Checklist
1. What Does “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed” Mean?
Part 1 – Technical SEO Audit (Current Page)
Part 2 – On-Page & Indexing SEO
Part 3 – Content & Authority SEO
Part 4 – Advanced SEO + AI + Monetization
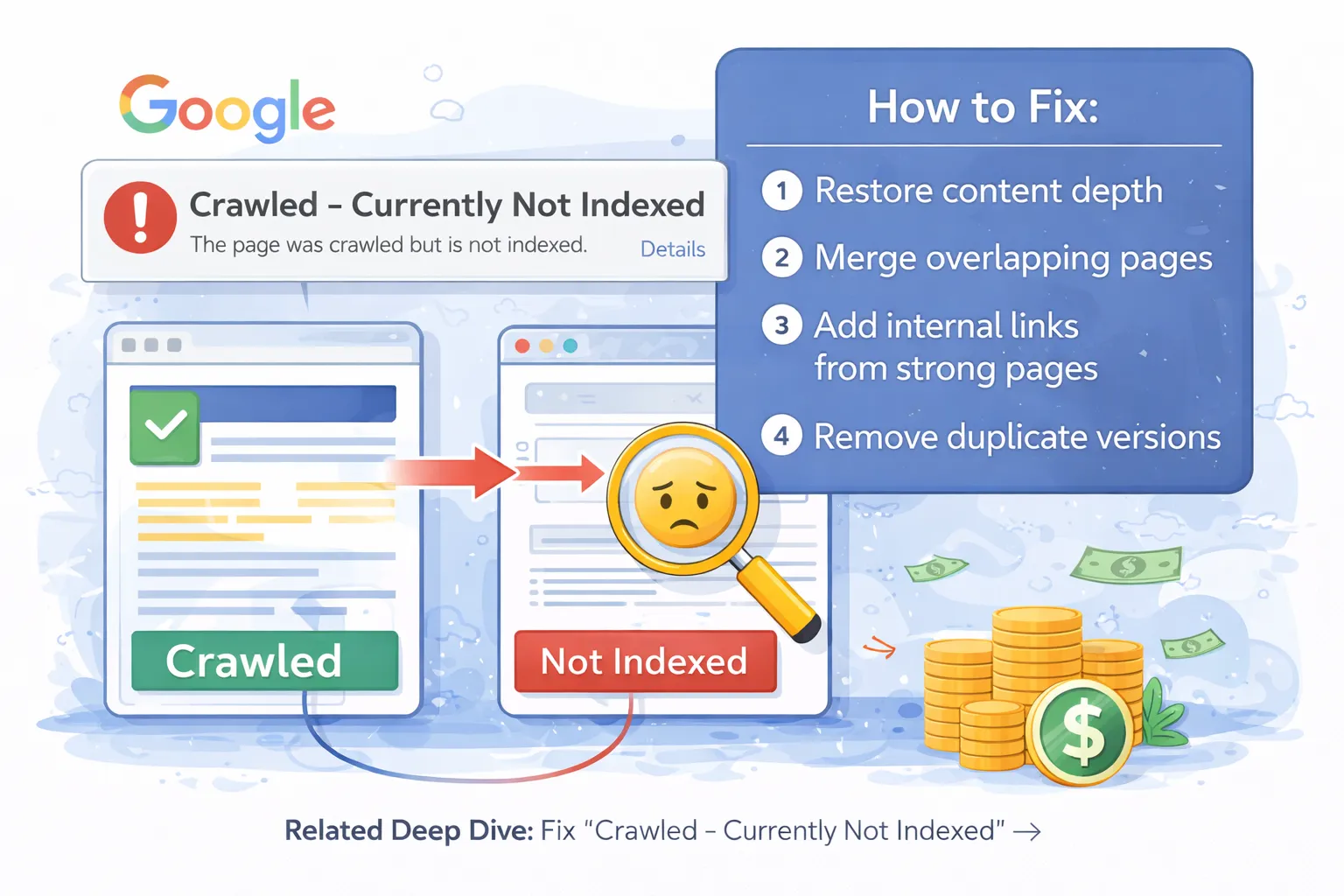
The status “Crawled – currently not indexed” inside Google Search Console (GSC) means:
Googlebot successfully visited your page, downloaded its content, processed it — but decided not to include it in Google's index.
This is NOT a penalty. It is Google's quality filtering system deciding that your page does not yet deserve to appear in search results.
Think of Google as a massive library. Crawling is like reading a book. Indexing is deciding whether that book deserves shelf space. Only the most useful, unique, and high-quality pages get indexed.
For new websites, this issue is extremely common. Even large websites frequently face it when:
- Publishing thin or duplicate pages
- Launching large content updates
- Migrating websites
- Changing URLs
👉 Related technical guide: Fix Page with Redirect Issue in Google Search Console
2. How Google Indexing Actually Works (Important)

To fix indexing problems properly, you must understand how Google processes pages.
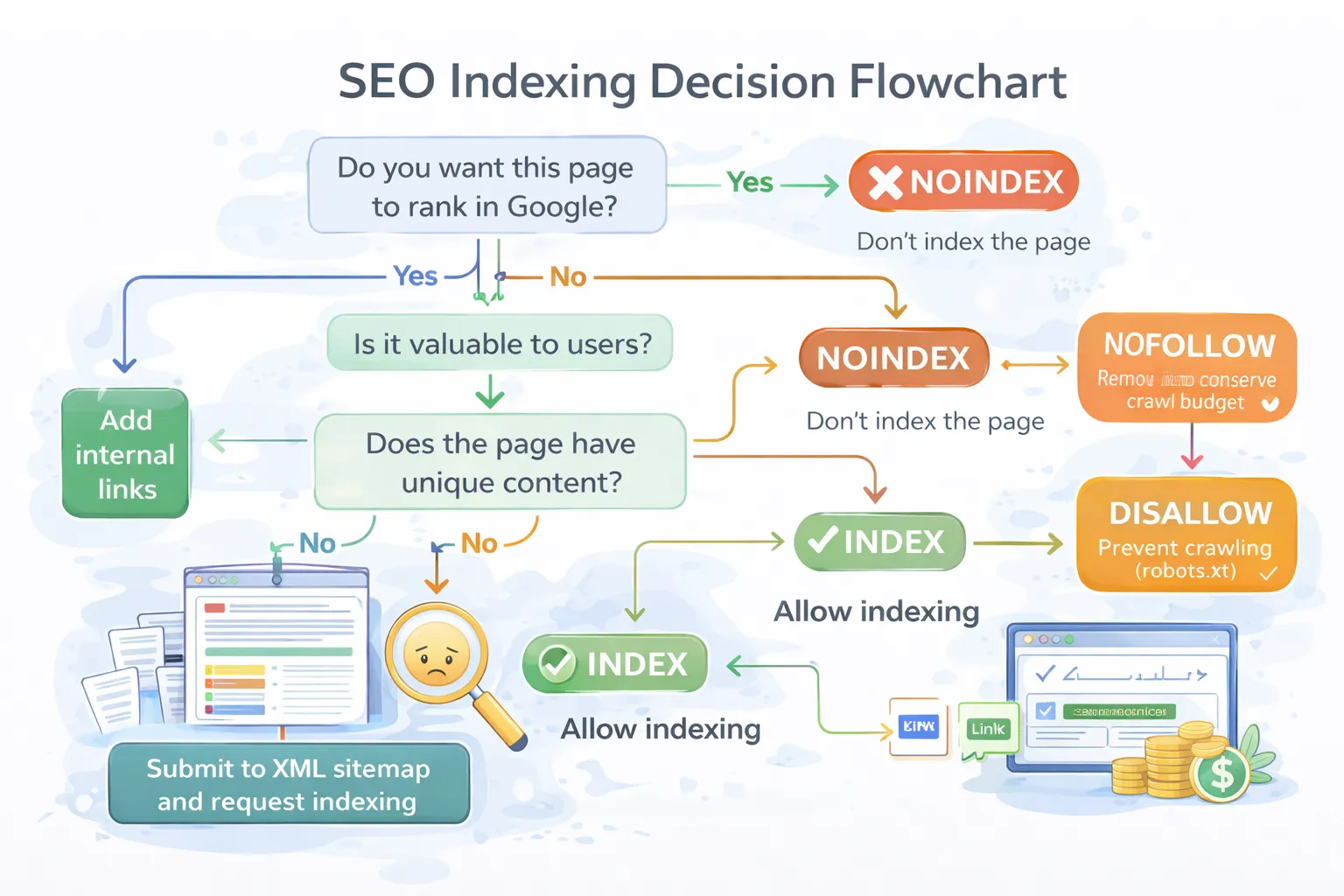
Google indexing works in 3 stages:
- Discovery — Google finds your URL via links, sitemap, or crawling.
- Crawling — Googlebot downloads your page.
- Indexing — Google evaluates quality & decides if page deserves ranking.
Your pages are failing at Stage 3 — Indexing Decision.
Google evaluates over **200+ quality and technical signals**, including:
- Content uniqueness
- Page value
- Internal links
- User engagement
- Authority signals
- Technical SEO health
👉 Complete SEO foundation guide: SEO Audit Checklist for New Websites
3. Why Google Crawls Pages But Doesn't Index Them
This is Google's filtering system at work. It prevents low-quality, duplicate, or unhelpful pages from polluting search results.
Most common reasons:
- Thin content
- Duplicate pages
- Low internal linking
- Weak site authority
- Soft 404 behavior
- Parameter-based URLs
- Low engagement metrics
Google is extremely selective in 2026. Simply publishing content does NOT guarantee indexing.
Google prefers fewer high-quality pages over millions of weak ones.For long-term ranking stability, this issue should be fixed alongside a content authority and internal linking strategy.
4. Root Causes of “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed”
1. Thin Content
Pages with fewer than 300–500 meaningful words rarely get indexed. Google wants **complete answers, not placeholders**.
Bad example:
- Short product descriptions
- Empty category pages
- Auto-generated pages
Good example:
- 1500–5000 word guides
- Detailed tutorials
- Case studies
2. Duplicate or Similar Content
If Google finds similar content elsewhere on your site, it will index only one version.
Common duplication sources:
- Category + tag pages
- Filter URLs
- Pagination pages
- Tracking parameters
3. Weak Internal Linking
Pages with zero internal links look **unimportant** to Google.
Your site structure should create a topic cluster model.
Example:
- Pillar: SEO Audit Guide
- Supporting: Indexing fixes, redirect guides, crawl budget blogs
👉 Technical linking guide: Technical SEO Checklist
4. Crawl Budget Wastage
Large sites often waste crawl budget on:
- Duplicate URLs
- Search result pages
- Filters
- Pagination loops
This reduces priority for important pages.
5. Low Authority Signals
New websites have little trust. Google may crawl your content but delay indexing until stronger authority signals appear.
Authority signals include:
- Quality backlinks
- Brand searches
- User engagement
- Social signals
5. SEO Fundamentals You Must Fix First
Before advanced fixes, ensure your **core SEO foundation** is strong.
- HTTPS working properly
- Fast page speed
- Mobile optimized layout
- Clean sitemap structure
- Correct canonical tags
- Zero redirect chains
👉 Full foundation guide: SEO Audit Checklist for New Websites
6. Quick Self Diagnosis Checklist
Before moving to technical solutions, check:
- Is my content better than top 10 competitors?
- Does this page deserve to rank?
- Is there duplicate version of this page?
- Is it linked internally?
- Does it provide real value?
If the answer is NO — Google will likely not index it.
What Comes Next?
Once pages are indexed, the next step is growth and monetization using an advanced SEO growth framework .
Now that you understand the meaning and causes, in PART 2 we will fix:
Part 1 – Technical SEO Audit (Current Page)
Part 2 – On-Page & Indexing SEO
Part 3 – Content & Authority SEO
Part 4 – Advanced SEO + AI + Monetization
- Technical SEO errors
- Canonical conflicts
- Redirect problems
- Indexing bottlenecks
- Crawl budget issues
We fix indexing, ranking, and authority problems for websites using enterprise SEO systems.
Get SEO Audit & Fix Plan